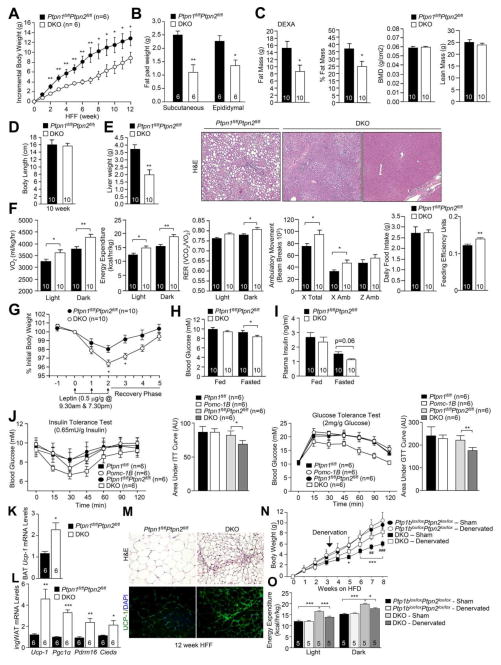
Figure 6. DKO mice are resistant to DIO.
8 week-old Ptpn1fl/flPtpn2fl/fl and DKO mice were HFF for 12 weeks and a) incremental body weight, b) fat pad weight, c) body composition, d) body length, e) liver weight and histology and f) oxygen consumption, energy expenditure, ambulatory activity, RER, food intake and feeding efficiency assessed. g) 12 week HFF mice were administered leptin and body weights monitored. Fed and fasted h) blood glucose and i) plasma insulin levels in 12 week HFF mice. j) Insulin and glucose tolerance tests in 12 week HFF mice. k–m) Browning gene expression, m) histology and immunohistochemistry in BAT or ingWAT from 12 week HFF mice. n–o) Ptpn1fl/flPtpn2fl/fl and DKO mice were HFF and either sham-operated or bilaterally denervated after 3 weeks, high fat feeding continued for 5 weeks and (n) incremental body weights and o) energy expenditure measured. Results are means ± SEM for the indicated number of mice and are representative of 3 independent experiments; significance determined using a–b, f–g, i–j, n–o) two-way ANOVA. n) * corresponds to floxed v/s DKO sham operated; # DKO sham v/s DKO denervated.