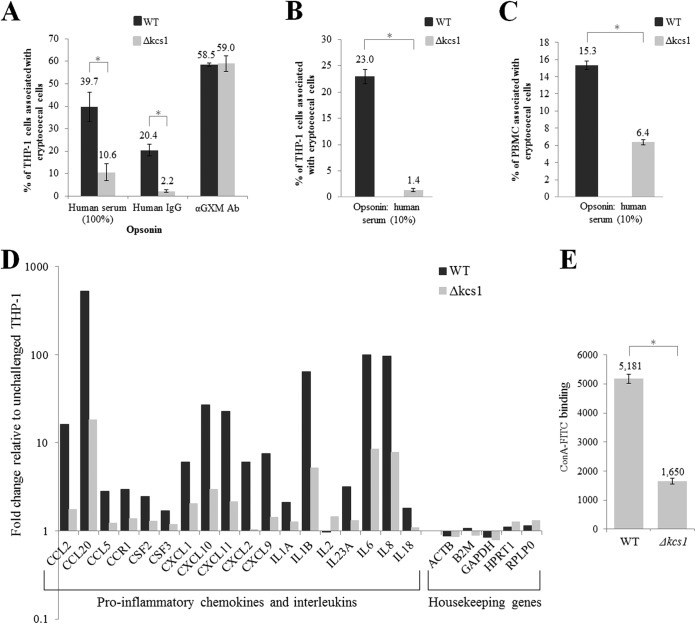
FIG 8 .
Reduced phagocytosis of Δkcs1 cells by monocytes correlates with reduced monocyte activation and reduced binding of concanavalin A. (A) Live FITC-labeled WT and Δkcs1 cells were opsonized with 100% serum, purified human IgG, or anti-GXM antibodies and cocultured with activated THP-1 monocytes for 4 h, and the extent of adhesion/uptake was measured by flow cytometry. (B) As in panel A, except that cells were heat killed and opsonized with 10% human serum. (C) As in panel B, except that CD14-positive monocytes within a PBMC preparation were used instead of THP-1 cells. (D) The expression of chemokine- and interleukin-encoding genes in activated THP-1 cells following coculture with serum-opsonized WT and Δkcs1 cells was quantified using an RT2 profiler PCR array designed for analysis of the antifungal response. The expression data were normalized to the expression of the housekeeping genes indicated and then calculated as the fold change from the expression of activated THP-1 cells that had not been coincubated with C. neoformans. (E) Each culture was incubated with ConA-FITC and the fluorescence quantified using flow cytometry. The bar graph represents the average fluorescence of WT and Δkcs1 cells. Except for those in panel D, all results represent the means and standard deviations of results from biological triplicates. *, P < 0.005 using an unpaired, two-tailed t test.