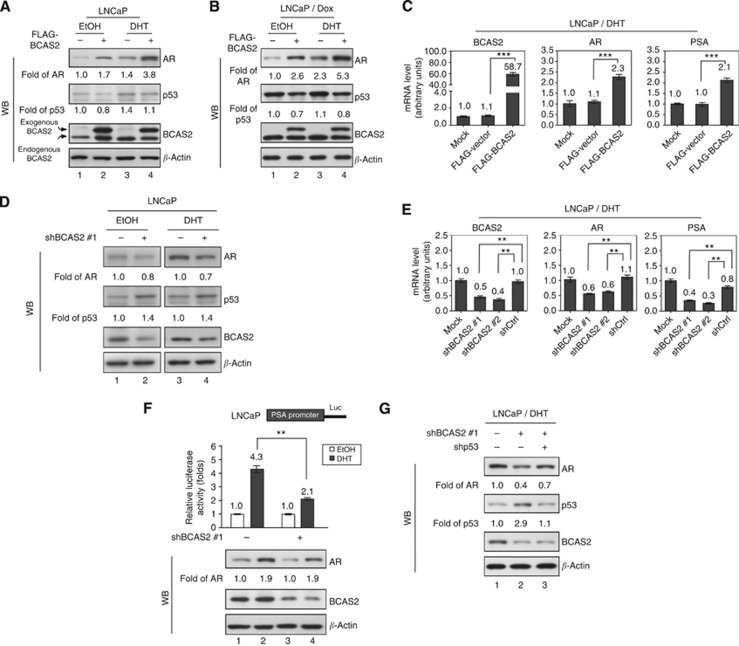
Figure 3.
BCAS2 enhances AR protein expression via a p53-dependent pathway. Overexpression of BCAS2 increases AR levels but decreases p53 protein, regardless of the presence of hormone. Following treatment with DHT (10 nM) or EtOH, LNCaP cells transfected with FLAG-BCAS2 were subjected to western blotting in the absence (A) or presence of 150 nM Dox (B). (C) Overexpression of BCAS2 increases AR and PSA mRNA levels. As shown in panel A, the levels of BCAS2, AR, and PSA mRNA were determined by quantitative PCR. ***: Student's t-test, P<0.001. (D) Reduction of BCAS2 decreases AR and increases p53 protein levels, regardless of the presence of hormone. (E) Depletion of BCAS2 expression reduces AR and PSA mRNA. **: Student's t-test, P<0.01. (F) The deprivation of BCAS2 reduces PSA promoter activity. Upper panel, all luciferase assays were carried out three times in independent experiments. Means±s.d. Lower panel, AR and BCAS2 protein expression. **: Student's t-test, P<0.01. (G) Depletion of BCAS2 decreases AR through a p53-dependent pathway. In the presence of DHT, LNCaP cells transfected with shBCAS2#1 along with shp53 or shCtrl were subjected to WB. The expression levels of AR and p53 protein quantified by UVP BioSpectrum-AC imaging software (UVP, Upland, CA, USA) were normalised to β-actin.