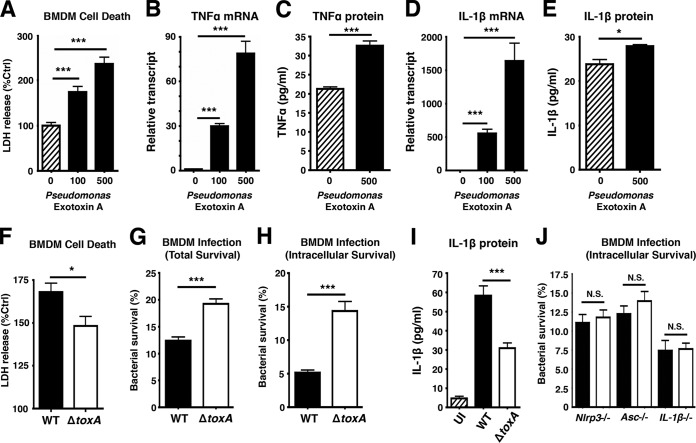
FIG 6 .
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ADP-ribosyltransferase exotoxin A triggers an inflammasome-dependent macrophage response to enhance bacterial killing. BMDMs were seeded in 24 wells in 2% FBS media a day before infection. (A) LDH released by BMDMs treated with 100 ng or 500 ng of P. aeruginosa exotoxin A (PEA) for 18 h. (B to E) RNA and supernatants from BMDMs were isolated for real-time qPCR and ELISA to assess transcript and protein levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in BMDMs treated with PEA. (F) LDH assay of supernatants harvested from BMDMs 2 h after P. aeruginosa infection (n = 4). (G and H) Total and intracellular killing of P. aeruginosa infected for 30 min at an MOI of ~20, followed by a 1-h streptomycin treatment (150 µg/ml). Cells were washed and incubated in serum-free media for 2 h to establish intracellular killing. (I) ELISA of IL-1β produced by P. aeruginosa-infected BMDMs 2 h postinfection. (J) BMDMs from Nlrp3−/−, Asc−/−, and IL-1β−/− mice were isolated to assess intracellular killing of P. aeruginosa (2 h post-gentamicin treatment). Error bars, SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; n = 3 (Student’s unpaired t test or one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test).