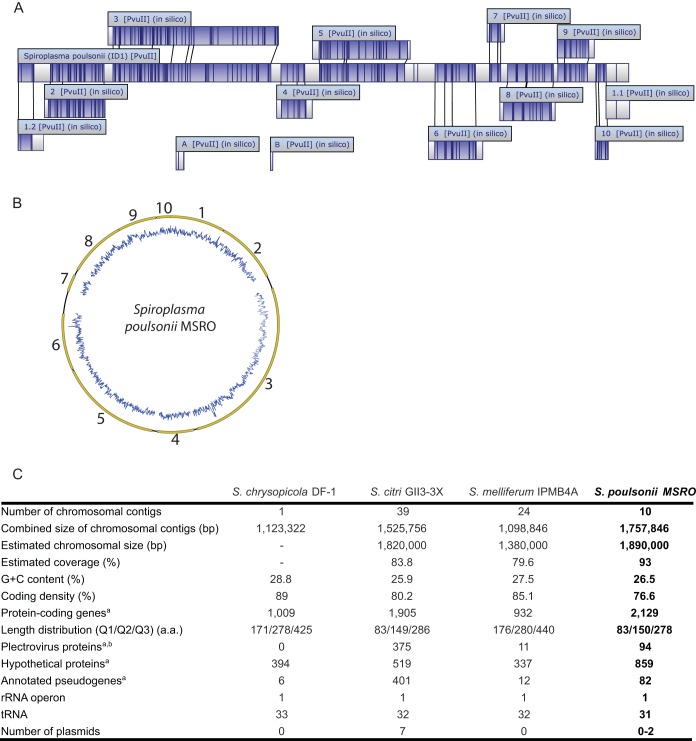
FIG 1 .
Draft assembly of the S. poulsonii MSRO genome. (A) Locations of the 12 contigs on the S. poulsonii chromosome as determined by optical mapping with MapSolver software (OpGen). Contigs A and B could not be placed on the chromosome. (B) Schematic representation of the S. poulsonii chromosome. Contigs (in yellow) were placed in order on the basis of the in silico alignment by optical mapping technology. The estimated length of the chromosome is ~1.89 Mb. GC content in depicted in blue. (C) Genome assembly statistics. The table shown was modified from reference 15. The superscript letter a indicates that for S. chrysopicola, S. melliferum, and S. poulsonii, putative pseudogenes were annotated with the “/pseudo” tag in gene feature as suggested by the NCBI GenBank guidelines and were not included in the total number of protein-coding genes. For S. citri, putative pseudogenes were annotated by adding the term “truncated” in the CDS product description field and were included in the total number of protein-coding genes. The superscript letter b indicates that most of the plectrovirus-related regions were excluded from the S. melliferum IPMB4A assembly because of unresolvable polymorphism, resulting in a lower number of plectroviral genes. The genome of S. chrysopicola does not contain any identifiable plectroviral fragments; this lineage was likely to have diverged prior to the plectroviral invasion of the common ancestor of S. citri, S. melliferum, and S. poulsonii. a.a., amino acids.