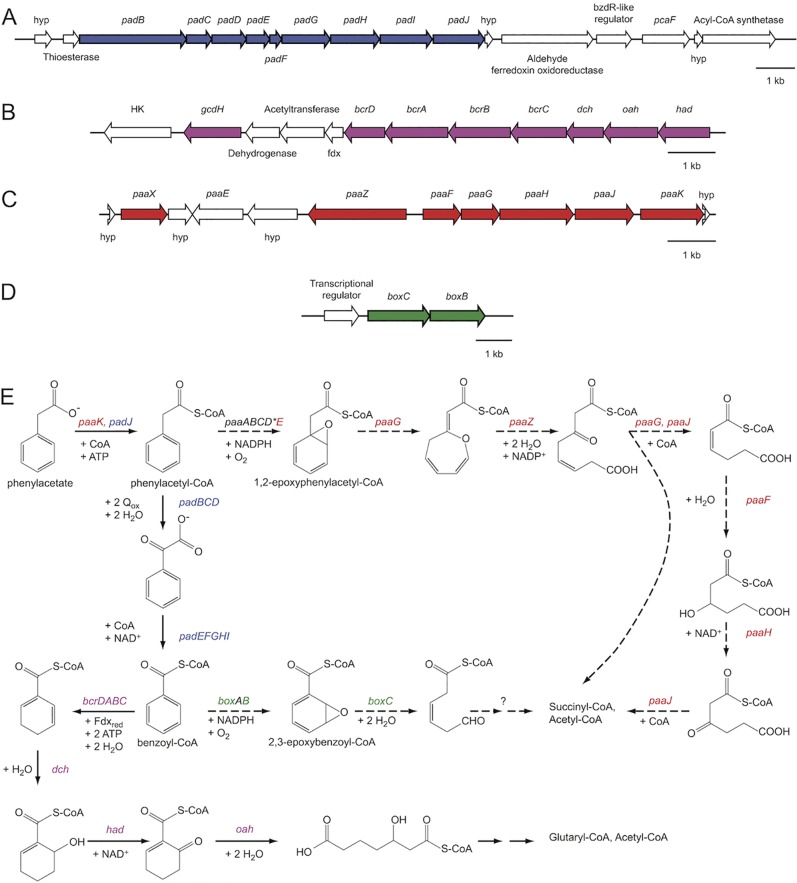
FIG 1 .
Genes and pathways of phenylacetate and benzoate degradation in S. selenatireducens CUZ. (A) pad gene cluster. (B) bcr gene cluster. (C) paa gene cluster. (D) box gene cluster. (E) Pathways of phenylacetate and benzoate degradation in strain CUZ. Red, paa gene cluster involved in the aerobic-hybrid pathway of phenylacetate degradation; blue, pad gene cluster involved in anaerobic phenylacetate degradation; purple, bcr gene cluster involved in anaerobic benzoate and phenylacetate degradation; green, box gene cluster involved in the aerobic-hybrid pathway of benzoate degradation; *, gene not found in strain CUZ. The anaerobic phenylacetate pathway is encoded by two gene clusters, the pad cluster (A; see Fig. S1A in the supplemental material) that converts phenylacetate to benzoyl-CoA (E), and the bcr cluster (B; see Fig. S1B) that degrades benzoyl-CoA to glutaryl-CoA and acetyl-CoA under anoxic conditions (E) (1, 4). The pad cluster (A) includes genes for the phenylacetate-CoA ligase (padJ), the phenylacetyl-CoA:acceptor oxidoreductase (padBCD), and the phenylglyoxylate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (padEFGHI). The bcr cluster (B) contains genes encoding a benzoyl-CoA reductase (bcrCBAD), an enoyl-CoA hydratase (dch), an oxoacyl-CoA hydrolase (oah), and a hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (had). The box (D; see Fig. S1D) cluster of aerobic-hybrid benzoate degradation encodes the beta subunit of the benzoyl-CoA oxygenase (boxB) and the 2,3-epoxybenzoyl-CoA dihydrolase (boxC). Genes involved in the aerobic-hybrid pathway of phenylacetate degradation (E) (1, 5) encode an oxepin-CoA hydrolase (paaZ), a 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA hydratase (paaF), a 1,2-epoxyphenylacetyl-CoA isomerase (paaG), a 3-hydroxyadipyl-CoA dehydrogenase (paaH), a 3-oxoadipyl-CoA thiolase (paaJ), and a phenylacetate-CoA ligase (paaK) (C; see Fig. S1C). Block arrows indicate the direction of transcription. Thin solid arrows, anaerobic pathways; thin dashed arrows, aerobic-hybrid pathways.