FIG 4 .
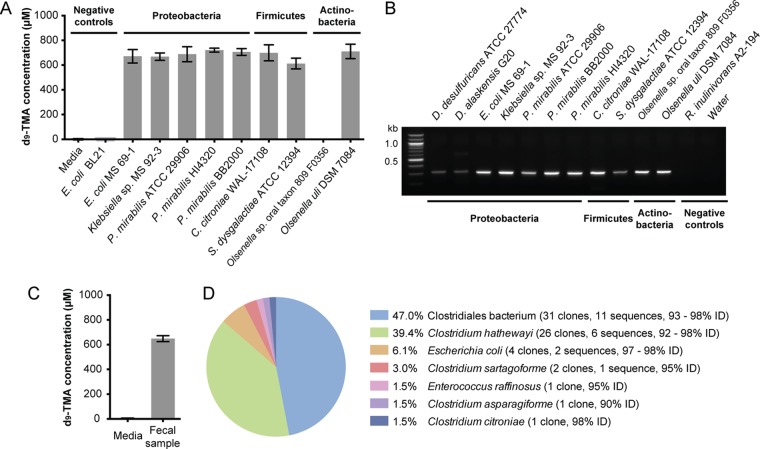
The cutC functional gene is diagnostic of anaerobic choline utilization and can be detected using degenerate PCR. (A) LC-MS quantification of d9-TMA produced by selected cutC-containing bacterial species grown in rich medium supplemented with d9-choline (1 mM); Olsenella sp. oral taxon 809 F0356 has cutC but is missing the gene encoding activase cutD. Each bar represents the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of d9-TMA from three cultures. (B) Agarose gel electrophoresis results for degenerate PCRs using cutC-specific degenerate primers and genomic DNA from representative cutC-containing, choline-utilizing strains and two sequenced organisms that lack cutC. (C) LC-MS quantification of d9-TMA produced ex vivo by a human fecal sample upon anaerobic incubation in BHI medium supplemented with (trimethyl-d9)-choline (1 mM) for 18 h at 37°C. Bar graphs represent the means ± SD of three independent incubations. (D) Abundances of translated cutC sequences in the 66-member clone library constructed from degenerate PCR with human gut metagenomic DNA and the percent identity to CutC proteins from sequenced isolates.