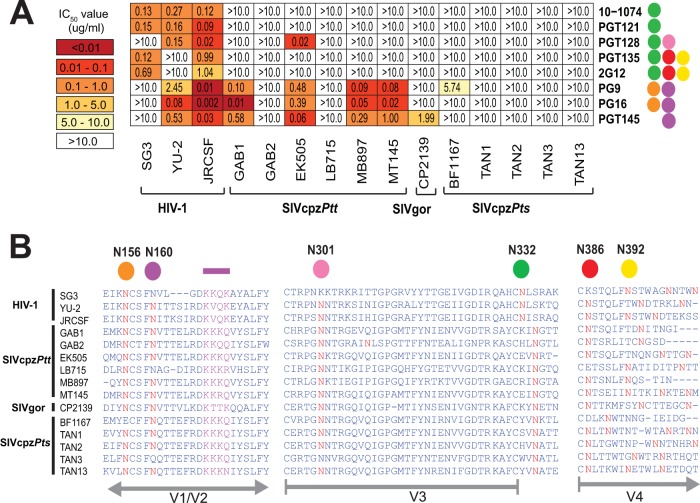
FIG 3 .
Neutralizing capacity of high-mannose-patch- and apex V2-directed antibodies. (A) The ability of peptidoglycan-associated monoclonal antibodies (listed on the right) to neutralize HIV-1, SIVcpz, and SIVgor strains (bottom) is shown. Numbers indicate IC50s (in micrograms per milliliter) in TZM-bl cells, averaged from three different experiments, with a heat map indicating the relative neutralization potency. Colored circles to the right of each antibody indicate the N-linked glycans that are important for their neutralizing activity (orange, N156; purple, N160; pink, N301; green, N332; red, N386; yellow, N392) (27, 28, 52, 81). The highest antibody concentration used was 10 µg/ml. (B) Conservation of glycans associated with bNab activity. An alignment of HIV-1, SIVcpz, and SIVgor Env protein sequences is shown, with predicted N-linked glycans (NXS/T) highlighted in red. Four residues comprising a lysine-rich motif in the V1/V2 strand (C), which together with glycans N156 and N160 form the core epitope for PG9, PG16, and PGT145, are highlighted in purple. N-linked glycans known to influence bNab binding are highlighted above the alignment, with HXB2 numbering in black. The positions of variable loops (V1/V2, V3, and V4) are shown in gray below the alignment.