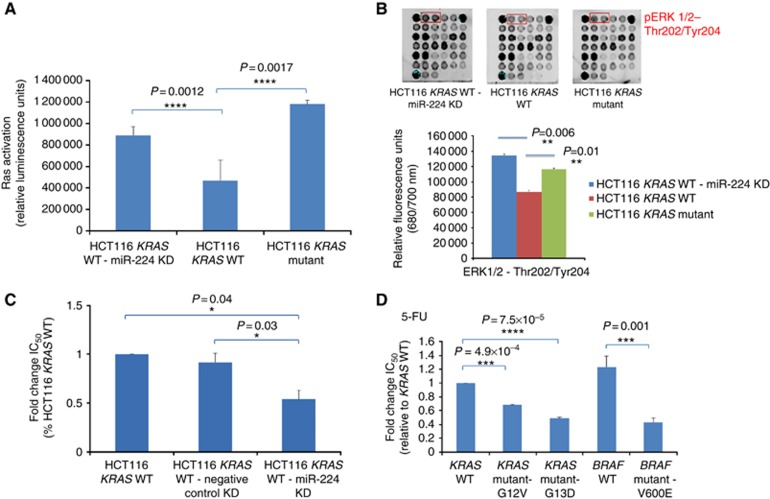
Figure 3.
Characterisation of miR-224 knockdown phenotypes. (A) A quantitative RAF-binding RAS ELISA was used, as described in Materials and Methods, to assess the influence of miR-224 knockdown on the amount of GTP-bound RAS in cell extracts from KRAS WT, KRAS WT-miR-224 knockdown and KRAS mutant HCT116 cells. Each sample was assessed in triplicate and data represent mean±s.e.m. of relative luminescence units. (B) PathScan intracellular signalling arrays were used, as described in Materials and Methods, to assess the influence of miR-224 knockdown on the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and additional substrates summarised in Supplementary Figure 2. Each sample was analysed in duplicate, with relative fluorescence at 680/700 nm quantified using a Li-Cor Odyssey fluorescence imaging system. MTT chemosensitivity assays were used, as described in Materials and Methods, to compare sensitivity to 5-FU in (C) KRAS WT HCT116 cells, cells transfected with a nonspecific negative control antagomir and miR-224 knockdown cells and (D) NIH3T3 mouse fibroblast cells stably expressing equivalent levels of WT KRAS and BRAF or KRAS (G12V and G13D) or BRAF (V600) mutant proteins. All experiments were performed in triplicate and IC50 values for each cell line calculated using GraphPad Prism (La Jolla, CA, USA).