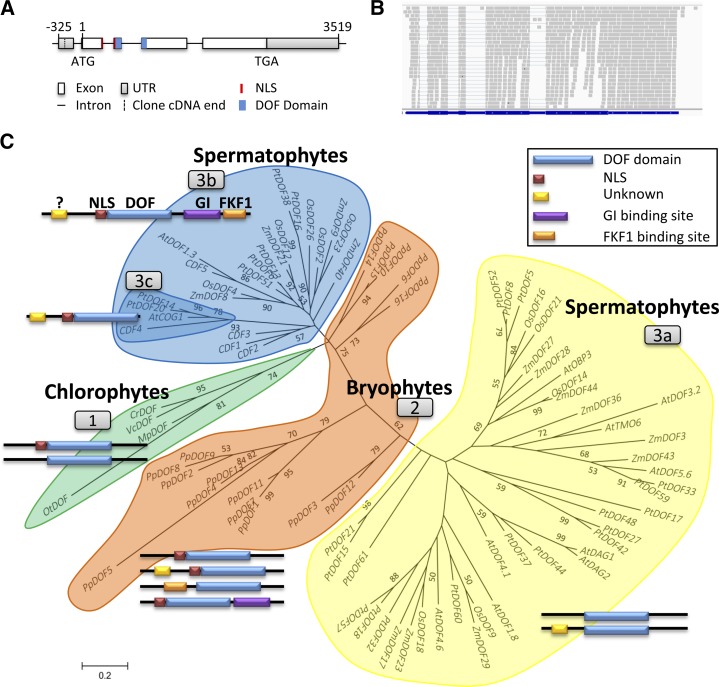
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree and domain evolution of DOF proteins. A, CrDOF gene structure. Squares represent exons, and lines represent introns. The DOF domain is in blue and the nuclear localization signal (NLS) is in red. B, Alignment of sequences obtained from RNAseq (gray) with the CrDOF gene structure (blue). C, Evolutionary relationship of 84 DOF proteins from eight species of the Viridiplantae linage. Three clusters pertaining to evolutionary grade are shown: chlorophytes (group 1), bryophytes (group 2), and spermatophytes (groups 3a–3c). Neighbor joining with the substitution model JTT + G 0.54 was the algorithm employed. The bootstrap number was 500. For abbreviations and protein accession numbers, see Supplemental Table S1. The domain structures of DOF proteins from each cluster are depicted beside each group. DOF domains are shown in blue, NLS in red, an unknown domain in yellow, and GI- and FKF1-binding sites in purple and orange, respectively. Only domains with a significant score in the MEME program are shown.