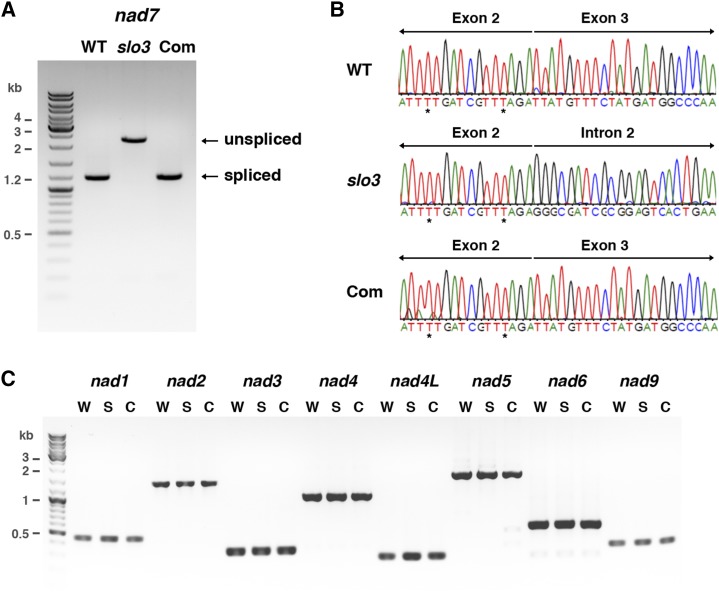
Figure 6.
RT-PCR and sequence analysis of nad7 transcripts in the slo3 mutant. A, Detection of fully processed nad7 transcripts by RT-PCR. The primers used for this experiment were located in exons 1 and 5, which would generate the 1,185-bp RT-PCR products for fully processed nad7 transcripts. Instead of 1,185 bp, the majority of the RT-PCR products in slo3 were the 2,248-bp unspliced form. Fully processed nad7 transcripts were restored in complemented plants (Com). B, Sequence histograms of RT-PCR products showing the junctions of spliced (exon 2-exon 3) and unspliced (exon 2-intron 2) nad7 transcripts from wild-type (WT), slo3, and complemented plants. Sequence analysis of the RT-PCR products confirmed that the 2,248-bp unspliced form contained exons 1 to 5 and the entire intron 2 of nad7 in the slo3 mutant. Asterisks indicate RNA editing sites. C, RT-PCR analysis of nad1, nad2, nad3, nad4, nad4L, nad5, nad6, and nad9 transcripts in wild type (W), slo3 (S), and complemented (C) plants. The primers used for this experiment were designed to amplify full-length or fully processed nad transcripts. These results confirmed that the splicing of nad7 intron 2 was specifically affected in slo3, whereas other mitochondrial nad transcripts were processed and accumulated normally in the mutant.