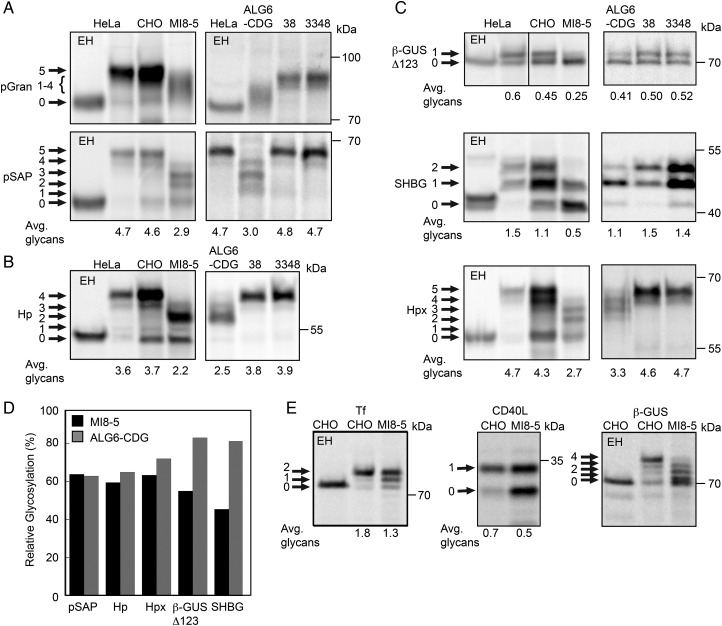
Fig. 2.
Hypoglycosylation of proteins in ALG6 deficient cell lines. Human (A–D) and Chinese hamster derived (A–E) cell lines were transfected with expression vectors for the following human glycoproteins: (A) progranulin (pGran-DDKHis) and prosaposin (pSAP-DDKHis); (B) haptoglobin (Hp-DDKHis); or (C) a β-glucuronidase derivative with a single C-terminal glycosylation site (β-GUSΔ123-MycDDK), sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) or hemopexin (Hpx-DDKHis); (E) transferrin (Tf-DDKHis), CD40 ligand (CD40L-Myc) or wild-type β-glucuronidase (β-GUS-MycDDK). The cells were pulse-labeled or pulse-chase labeled as described in Materials and Methods. The glycoprotein substrates were precipitated with anti-DDK, anti-Myc or anti-SHBG sera and then resolved by SDS–PAGE. Endogenous progranulin and prosaposin were immunoprecipitated from fibroblasts and HeLa cells using anti-pSAP and anti-pGRAN sera. EH designates treatment with endoglycosidase H. Quantified values below gel lanes (A–C, E) are the average number of glycans per protein chain from two or more experiments. (D) The relative glycosylation efficiency (%) of substrates that were assayed in both ALG6-deficient cell lines was calculated by averaging the glycosylation efficiency of the mutant cell line relative to the relevant wild-type control cell line.