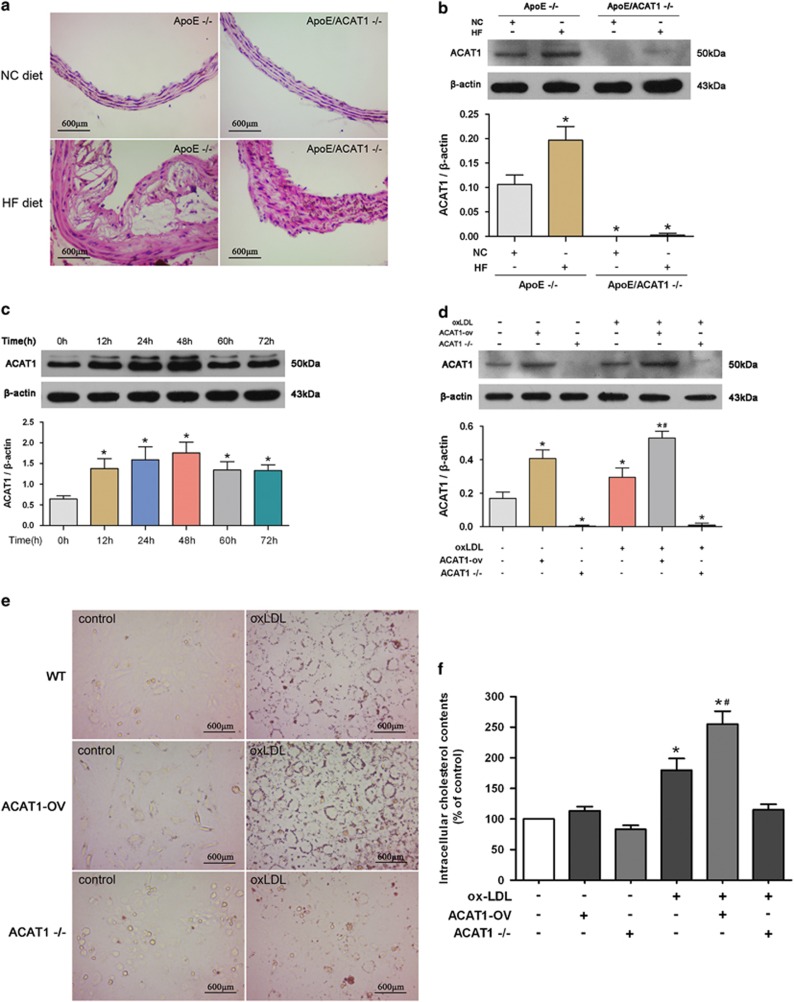
Figure 1.
ACAT1 has a critical role in atherosclerotic plaque formation and in oxLDL-induced VSMC foam cell formation. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining on cross-sections from representative aortas are presented. HF diet significantly induced atherosclerotic plaque formation in ApoE−/− mice. ApoE/ACAT1−/− mice only displayed intimal hyperplasia in response to HF diet. (b) ACAT1 expression in aortas detected by western blot. HF diet induced ACAT1 expression in ApoE−/− mice but not in ApoE/ACAT1−/− mice (*P<0.05 versus ApoE−/− mice with NC diet). (c) Primary VSMCs from WT mice were incubated with oxLDL (80 μg/ml) for different times (0, 12, 24, 48, 60 or 72 h). ACAT1 level was increased in a time-dependent manner, with an obvious effect at 48 h after oxLDL challenge (*P<0.05 versus 0 h). (d–f) Primary VSMCs from WT mice were manipulated with adenovirus-mediated overexpression (ACAT1-ov) or knockout-mediated gene deficiency (ACAT1−/−) and then treated with oxLDL for 24 h (d). Cultured VSMCs in basal conditions displayed low levels of lipid droplet accumulation (e) and intracellular cholesterol (f), which were significantly elevated by oxLDL. ACAT1 overexpression increased, whereas ACAT1 deficiency reduced, the oxLDL-induced lipid droplet accumulation (e) and intracellular cholesterol elevation (f) (*P<0.05 versus control WT-VSMCs; #P<0.05 versus WT-VSMCs with oxLDL challenge). Results were presented as mean±S.D. (error bars) of three independent experiments