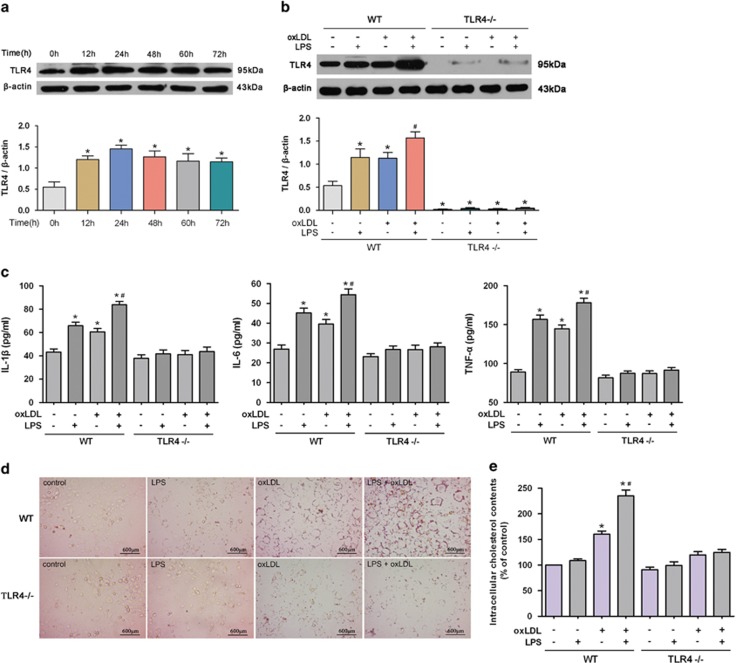
Figure 3.
TLR4-mediated inflammation is required in oxLDL-induced VSMC foam cell formation. (a) Primary VSMCs from WT mice were incubated with oxLDL (80 μg/ml) for different times (0, 12, 24, 48, 60 or 72 h). TLR4 level was increased in a time-dependent manner, with an obvious effect at 24 h after oxLDL challenge (*P<0.05 versus 0 h). (b–e) Primary VSMCs from WT and TLR4−/− mice were treated with oxLDL and/or LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. OxLDL significantly increased the levels of TLR4 (b) and proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α) (c) in VSMCs from WT mice, which were further elevated by LPS. In contrast, oxLDL and LPS failed to induce the expression of TLR4 (b) and proinflammatory cytokines (c) in VSMCs from TLR4−/− mice. LPS markedly increased oxLDL-induced lipid droplet accumulation (d) and intracellular cholesterol elevation (e) in VSMCs from WT mice. By contrast, oxLDL and LPS failed to significantly increase lipid droplet accumulation (d) and intracellular cholesterol level (e) in VSMCs from TLR4−/− mice (*P<0.05 versus control WT-VSMCs; #P<0.05 versus WT-VSMCs with oxLDL challenge). Results were presented as mean±S.D. (error bars) of three independent experiments