FIGURE 7:
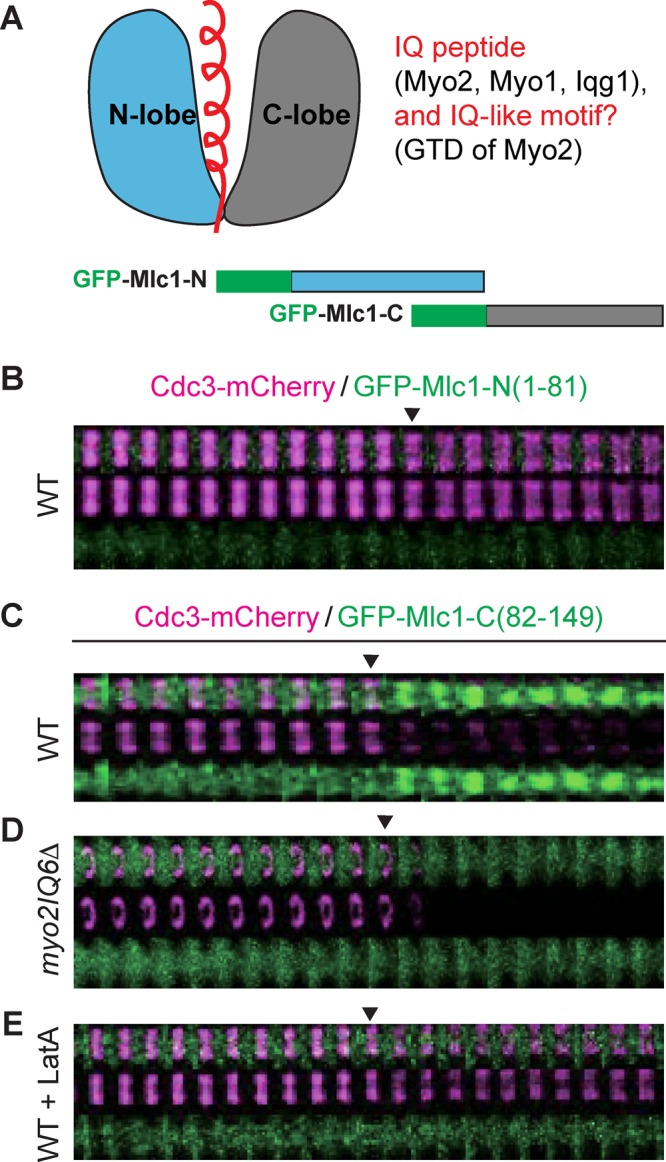
Localization of the C-lobe of Mlc1 to the bud neck depends on Myo2 and actin filaments. (A) Schematics of Mlc1 structure and its binding partners (top) and of GFP‑tagged N‑ and C‑lobes of Mlc1 (bottom). The helical IQ peptide or IQ‑like motif (top left) from the binding partners of Mlc1 (top right) are highlighted in red. (B) Time-lapse analysis of the N‑lobe of Mlc1 (amino acids 1–81) and Cdc3 during the cell cycle in WT cells (YEF7208; CDC3‑mCherry, GFP‑MLC1‑Nterm). (C–E) Time-lapse analysis of the C‑lobe of Mlc1 (amino acids 82–149) and Cdc3 during the cell cycle in WT (YEF7209; CDC3‑mCherry, GFP‑MLC1‑Cterm; C), myo2IQ6Δ (YEF7245; myo2IQ6Δ CDC3‑mCherry, GFP‑MLC1‑Cterm; (D), and LatA‑treated WT (YEF7209; E) cells.
