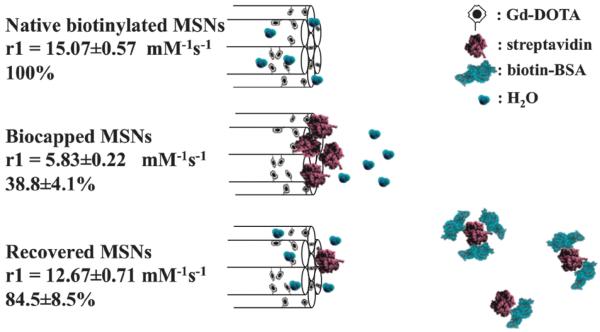
Fig. 3.
Schematic summary of MSN relaxivity gating. Externally biotinylated Gd-doped MSNs enjoy good water accessibility and a high relaxivity (15.07 ± 0.57 mM−1 s−1) that can be reversibly capped by the steric bulk of a bound STV (5.83 ± 0.22 mM−1 s−1; <40% of the original value). In the presence of low μM biotinylated BSA, the gating protein is competed off the particle surface and relaxivity recovers to 12.67 ± 0.71 mM−1 s−1 (84.5 ± 8.5% of original value). Error here represents cumulative error arising from triple repeats of relaxivity assessment (across at least three different sample concentrations at 7 T and 20 °C) and ICP quantification.