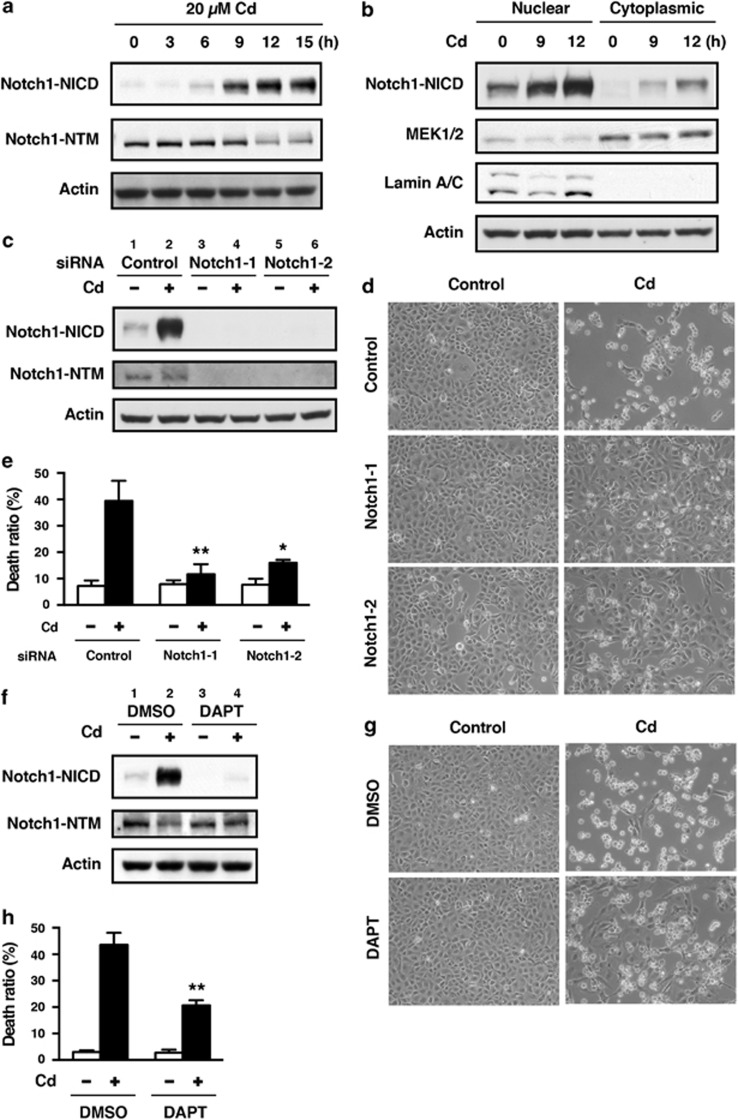
Figure 1.
Involvement of Notch1 signaling in CdCl2-induced cellular damage in HK-2 cells. (a and b) Cells were incubated with 20 μM CdCl2 (Cd) for the indicated time. The untreated control is labeled 0 h. Cell lysates were subjected to western blotting using antibodies against Notch1-NICD, Nohch1-NTM, and actin (a). Equal amounts of protein (20 μg) in nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were subjected to western blotting using antibodies against Notch1-NICD, MEK1/2, lamin A/C, and actin. MEK1 and lamin A/C served as a loading control for cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts, respectively (b). (c–e) Cells transfected with control siRNA, Notch1 siRNA-1, or Notch1 siRNA-2 were incubated with or without 20 μM CdCl2 (Cd) for 12 h (c), 24 h (d), or 30 h (e). Cell lysates were subjected to western blotting using antibodies against Notch1-NICD, Notch1-NTM, and actin (c). Phase-contrast micrographs were taken (d). The viability of cells was determined by trypan blue exclusion assay. Each value is the percentage of trypan blue-positive cells and reflects the mean±S.D. of three experiments with duplicate assays in each experiment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus CdCl2-treated cells transfected with control siRNA (e). (f–h) Cells were incubated with 0.1% DMSO or 40 μM DAPT for 1 h and then incubated with or without 20 μM CdCl2 (Cd) for 12 h (f) or 30 h (g and h). Cell lysates were subjected to western blotting using antibodies against Notch1-NICD, Notch1-NTM, and actin (f). Phase-contrast micrographs were taken (g). The viability of cells was determined by trypan blue exclusion assay. Each value is the percentage of trypan blue-positive cells and reflects the mean±S.D. of three experiments with duplicate assays in each experiment. **P<0.01 versus CdCl2-treated cells incubated with DMSO (h). Immunoblots shown are representative of at least three independent experiments