Figure 8.
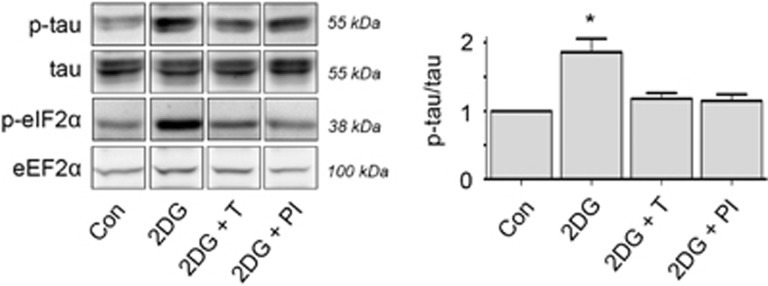
Inhibition of UPR prevents p-tau upon metabolic stress. Differentiated SK-N-SH cells were treated 20 h with 2DG alone or in the presence of TUDCA (2DG+T), a UPR inhibitor or a selective PERK inhibitor (2DG+PI). Representative western blot of n=3 is shown. Tau Ser396 phosphorylation (p-tau) is significantly increased after treatment with 2DG, but is not significantly increased in presence of TUDCA or the PERK inhibitor. Quantification of p-tau is relative to total tau levels. P-eIF2α, the first downstream target of activated PERK, is shown as an indicator of UPR activation. eEF2α is used as a loading control. This experiment shows that p-tau can be prevented by inhibition of the UPR via the PERK pathway (*P<0.01)
