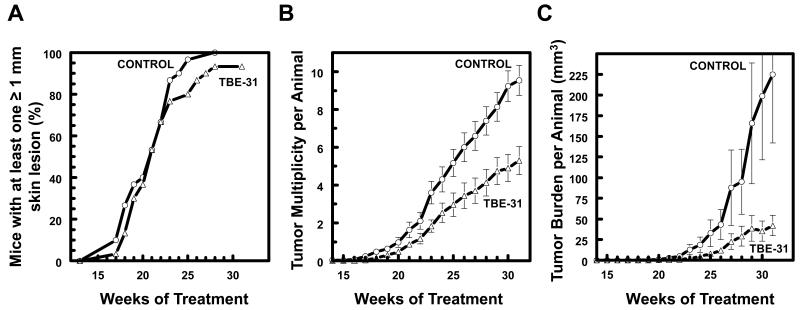
Figure 6. Pharmacological upregulation of Nrf2 by TBE-31 protects against cutaneous carcinogenesis mediated by solar-simulated UV radiation in mice receiving azathioprine therapy.
WT SKH-1 hairless mice (n=30) were treated with azathioprine (1 mg/kg/day, orally, dissolved in the drinking water), and either vehicle (80% acetone) or TBE-31 (40 nmol per mouse, twice a week, topically, in 200 μl of 80% acetone). Two weeks after beginning of treatment with azathioprine and TBE-31, the animals were exposed chronically to solar-simulated UV radiation (comprised of 2 J/cm2 UVA and 90 mJ/cm2 UVB), twice a week for a further 15 weeks. Irradiation was then stopped, but treatment with both azathioprine and TBE-31 was continued for the duration of the experiment. During the subsequent 16 weeks, the appearance of tumors was monitored weekly, the lesions were mapped, counted, and their volumes determined. The graphs show tumor incidence (A), multiplicity (B) and burden (C). The number of tumors per mouse (multiplicity) and the tumor volume are expressed as average values ± S.E.M. based on the total number of animals at risk.