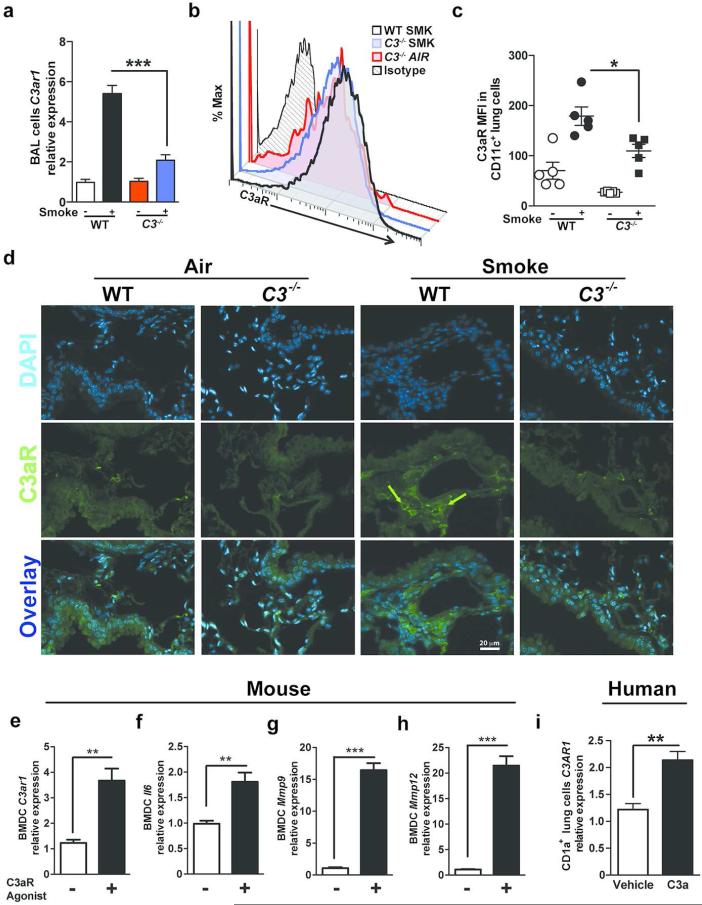
Figure 3. Expression of C3aR in mouse lung inflammatory cells and human mDCs.
WT and C3 deficient mice were exposed to cigarette smoke or air for 6 months. (a) Expression of C3ar1 mRNA in BAL cells isolated from WT or C3−/− mice exposed to air or cigarette smoke was measured by quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qPCR). ***P<0.001, as determined by the one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison. Representative (b) and cumulative data (c) measuring C3aR mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) in single lung cells gated on B220− CD11c+ population using flow cytometry. *P<0.05, as determined by the one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison. (d) Representative photomicrograph of WT and C3−/− mouse lung tissue exposed to six months of smoke or air immunostained for expression of C3aR (green) or nuclei (blue; DAPI). Scale bar: 20μm. Green arrows indicate C3aR+ cells. (e) to (h) Mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs; 2×105) were treated with C3aR Agonist (CAS 944997-60-8; 20ng/ml) or vehicle (2% DMSO) for 48 hours. Expression level of C3aR1, Il6, Mmp9 and Mmp12 mRNA were measured using qPCR (n=4 in each group; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, as determined by student t test. (i) Human CD1a+ lung mDCs (2×105) were treated with purified human C3a (40ng/ml) for 24 hours or vehicle (media). Expression level of C3AR1 mRNA was measured by quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qPCR). n=3; **P<0.01, as determined by student t test. All gene expressions were normalized to 18S ribosomal RNA expression and analyzed by ΔΔCt. Results are represented as mean±s.e.m, from 3 independent experiments with 4-5 mice in each group (a-d).