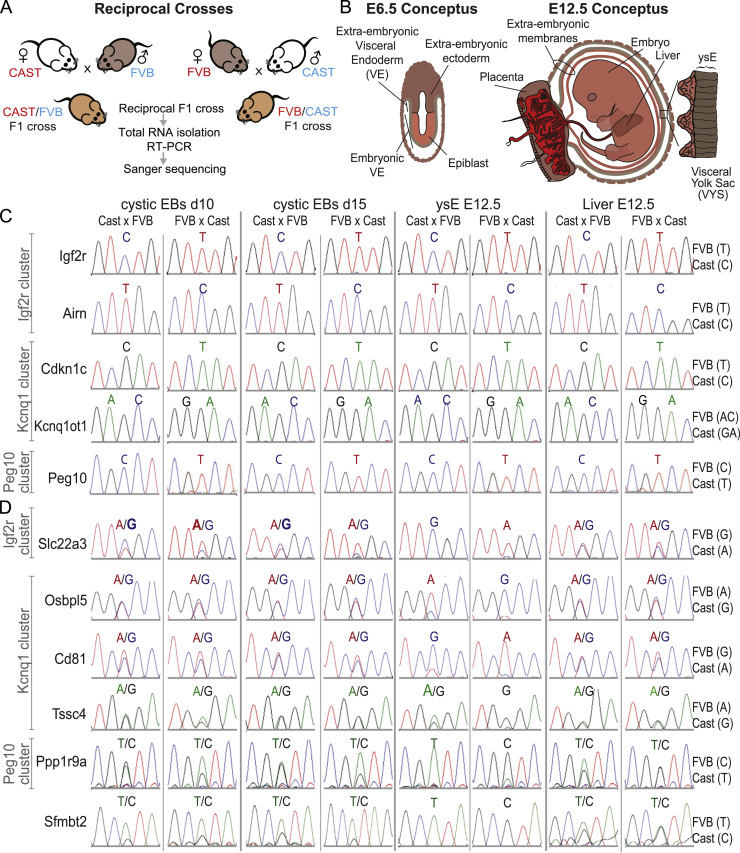
Fig. 2.
Cystic EBs show multi-lineage (ML) but not extra-embryonic lineage (EXEL) specific imprinted gene expression. (A) The breeding scheme used to obtain reciprocal crosses between the FVB/N (FVB) and CAST/EiJ (CAST) mouse strains for imprinted expression analysis using single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). (B) Embryos at E6.5 and E12.5 indicating embryonic and extra-embryonic tissues (VYS diagram adapted from Hudson et al. (2011)). (C) The ML imprinted genes Igf2r, Cdkn1c (maternally-expressed), and Kcnq1ot1, Airn, Peg10 (paternally-expressed) that represent 3 out of 4 imprinted clusters that contain EXEL genes, show the expected reciprocal imprinted expression pattern in cystic EBs, E12.5 yolk sac endoderm (ysE) and E12.5 fetal liver. The expressed SNP is shown above each Sanger sequencing chromatogram, FVB and CAST alleles are indicated on the right. (D) The EXEL genes Osbpl5, Cd81, Tssc4, and Ppp1r9a from the Kcnq1 and Peg10 imprinted clusters show biallelic expression in cystic EBs. The solo EXEL gene Sfmbt2 shows a strain bias between FVB and CAST so biallelic expression in cystic EBs was validated in B6/129 ES cells (Fig. S2B). The Slc22a3 EXEL gene from the Igf2r cluster shows a reciprocal bias in cystic EBs with very low expression requiring 40 PCR cycles and multiple reactions to acquire enough DNA for sequencing. Each EXEL gene shows imprinted expression in E12.5 ysE and biallelic expression in E12.5 fetal liver. SNPs are displayed above the chromatograms with a single base indicating robust imprinted expression, both SNP bases indicating biallelic expression, and both SNP bases with one in bolded font indicating biased expression. The maternal allele is written on the left.