Figure 4. RhoA pathway regulation of actin-related pericyte functions involved in development of chronic rejection.
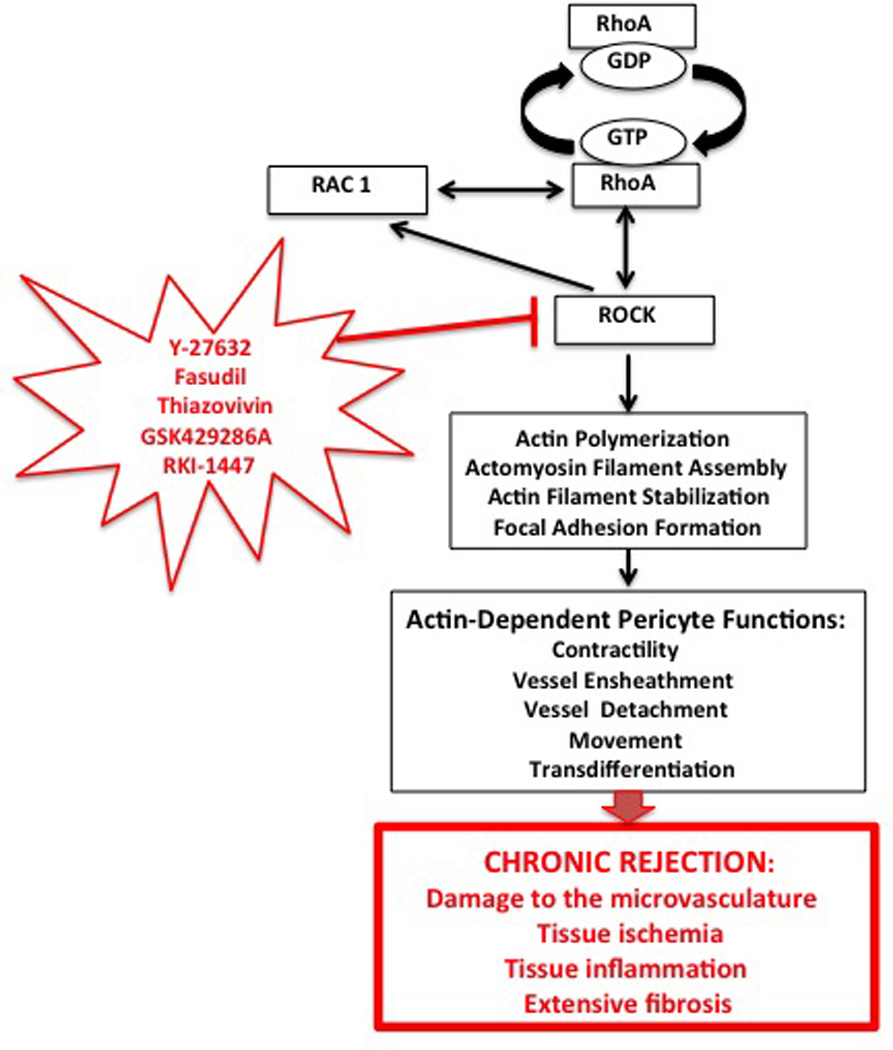
RhoA regulates, through its downstream effector ROCK (containing ROCK 1 and ROCK 2 isoforms) actin filament polymerization and organization, which in turn regulate various functions of pericytes. In addition, RhoA (either directly or through ROCK) cross talks with Rac1 pathway. There are several inhibitors of ROCK (ROCK 1, ROCK 2 or both), which are known, from rodent or human clinical studies, to influence actin-related cellular functions in immune response and transplantation (129, 130). Because many of pericyte functions such as movement, contractility, interaction with vessel endothelium and transdifferentiation into collagen producing myofibroblasts also depend on actin cytoskeleton, these inhibitors, via targeting pericytes, have a potential to be used as the anti-inflammation and anti-chronic rejection therapeutics.
