Table 1. Contributing factors to annual PDI.
| Pentad | PDI (%) | I (%) |
N+ (%)
(%)
|
N (%) |
 (%)
(%)
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993–1997 w.r.t. mean | 28.6 | −22.2 | 50.8 | 23.4 | 27.4 |
| 1998–2002 w.r.t. mean | −30 | −15.8 | −14.2 | 0.2 | −14.4 |
| 2003–2007 w.r.t. mean | 17.8 | 30.8 | −13 | −11.6 | −1.4 |
| 2008–2012 w.r.t. mean | −16.6 | 6.8 | −23.4 | −15.8 | −7.6 |
| [2008–2012] w.r.t. [1993–1997] | −45.2 | 29 | −74.2 | −39.2 | −35 |
PDI, Power Dissipation Index; w.r.t., with respect to. Contributions of the observed typhoon case number (N), duration (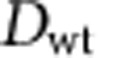 ) and intensity (I) to the western North Pacific annual PDI, based on the method from Emanuel 2007 ref. 18. The top 4 rows are changes in each pentad w.r.t. the long-term mean (1993–2012). The last row is the change in the most-recent pentad (2008–2012) w.r.t. the 1st pentad in the early 1990s (1993–1997).
) and intensity (I) to the western North Pacific annual PDI, based on the method from Emanuel 2007 ref. 18. The top 4 rows are changes in each pentad w.r.t. the long-term mean (1993–2012). The last row is the change in the most-recent pentad (2008–2012) w.r.t. the 1st pentad in the early 1990s (1993–1997).
