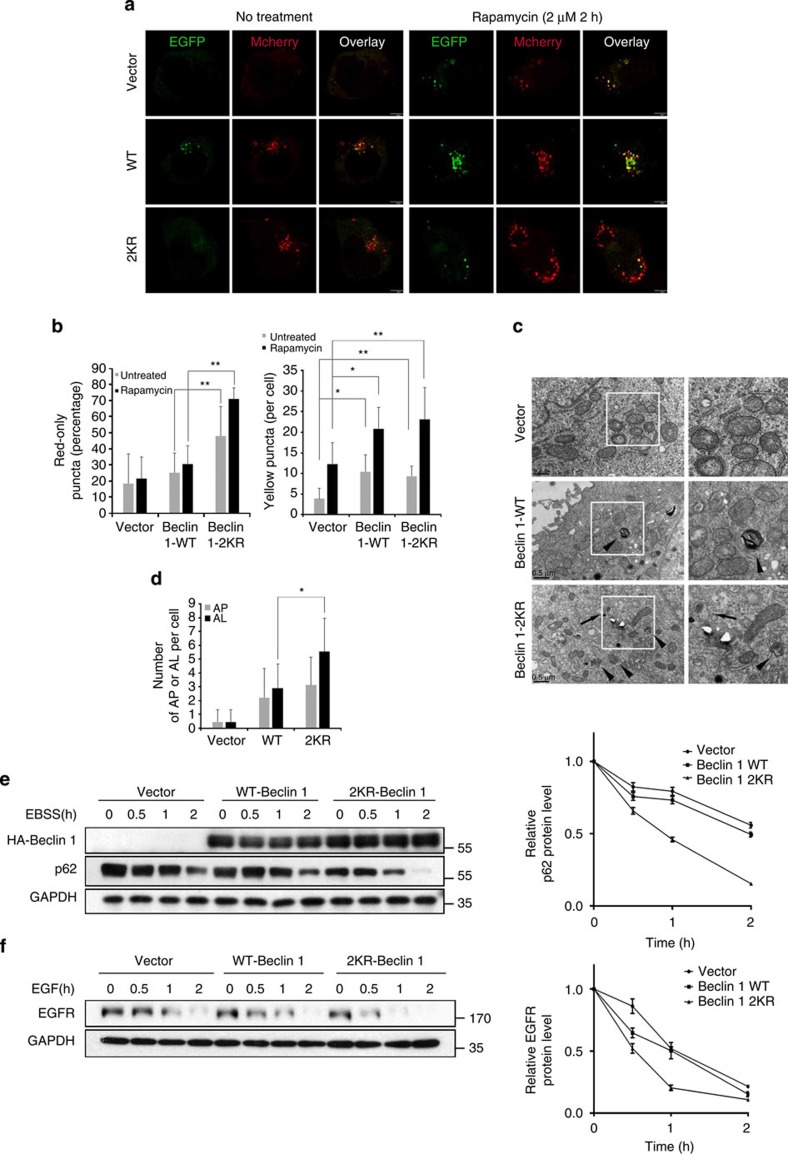
Figure 5. Autophagosome maturation and endocytic trafficking in Beclin 1–2KR-expressing cells.
(a) Beclin 1–2KR mutant promotes the maturation of autophagosomes. 293T cells stably expressing Vector control, Beclin 1 WT or 2KR were transfected with mCherry-EGFP-LC3 in the absence or presence of rapamycin (2 μM). Scale bars, 5 μm. (b) Quantitation of mCherry-LC3-only puncta and the mCherry-EGFP overlay puncta in 293T cell lines treated as in a. Bars represent mean±s.d. of 50 cells; five independent experiments, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (Student's t-test). (c) Electron microscopy analysis of autophagosomes and autolysosomes. MCF7 cells stably expressing Beclin 1 (WT or 2KR) or Vector grown in normal medium was subjected to electron microscopy analysis. The arrows indicate autophagosomes (AP) and the arrowheads indicate autolysosomes (AL). Scale bar, 0.5 μm. (d) Quantitation of AP and AL in MCF7 cell lines as in c. Bar are mean ±s.d. of 20 cells; three independent experiments, *P<0.05 (Student's t-test). (e) The effect of Beclin 1–2KR mutant on p62 turnover. MCF7 cells stably expressing vector control, Beclin 1 WT or 2KR were treated with EBSS for the indicated times. The band intensity was measured in three independent experiments and the mean±s.d. are shown (down panel). (f) EGFR degradation. MCF7 cells stably expressing vector control, Beclin 1 WT or 2KR were serum-starved for 24 h, and then treated with EGF (200 ng ml−1) for the indicated times. The band intensity was measured in three independent experiments and the mean±s.d. are shown (down panel).