Figure 9. The possible signal pathways regulated by HDAB in cervical cancer cells.
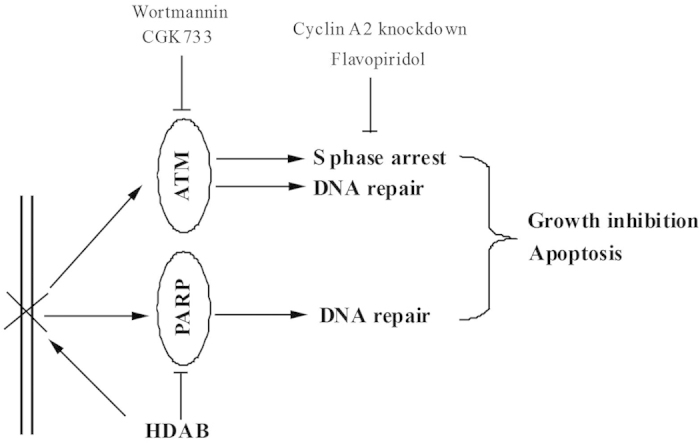
HDAB treatment activates the ATM-dependent DNA damage response and induces S phase arrest. An ATM kinase inhibitor, a CDK2 inhibitor and cyclin A2 siRNA can significantly increase the HDAB-induced apoptosis of cervical cancer cells. In addition, HDAB can function as an inhibitor of PARP to impair DNA repair, thereby enhancing cell death.
