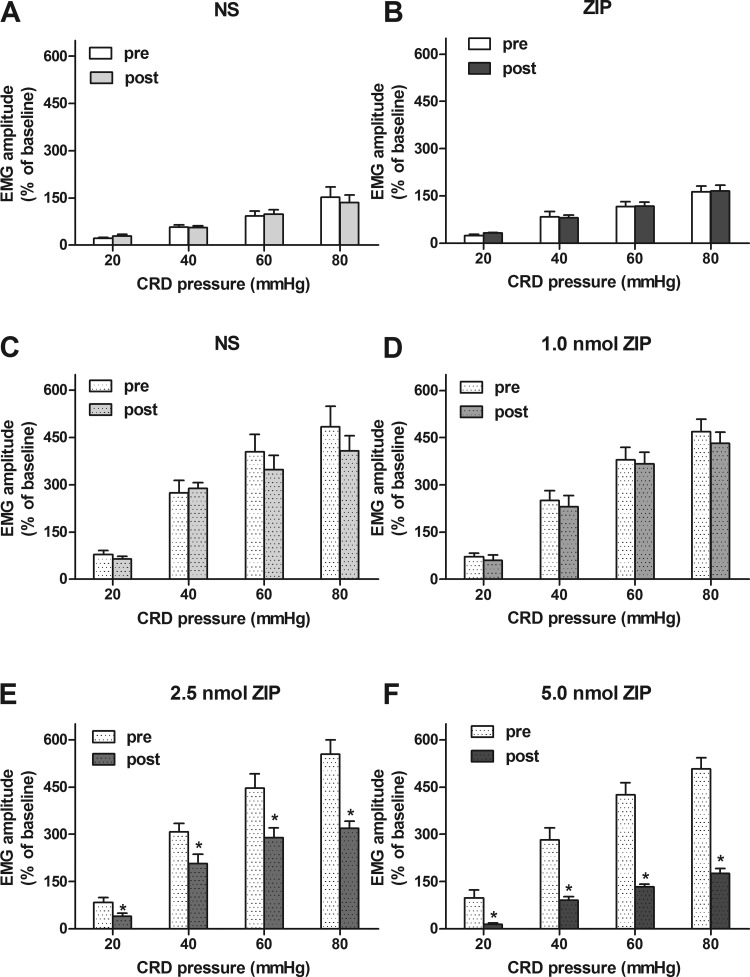
Fig. 4.
Effect of bilateral intrahippocampal injections of ZIP on EMG in rats. A: the statistical graph of the electromyographic amplitude after bilateral intrahippocampal injections of normal saline (NS; 2 μl each side) in controls. B: the statistical graph of the electromyographic amplitude after bilateral intrahippocampal injections of 5.0 nM ZIP (2 μl each side) in controls. Bilateral intrahippocampal injections of ZIP had no influence on EMG in controls. C: the statistical graph of the electromyographic amplitude after bilateral intrahippocampal injections of NS (2 μl each side) in rats of NMS. D–F: the statistical graph of the electromyographic amplitude after bilateral intrahippocampal injections, 1, 2.5, and 5 nM ZIP (2 μl each side) in rats of NMS. ZIP dose dependently inhibited the visceral hypersensitivity in rats of NMS; n = 8. *P < 0.05 vs. pre-drug.