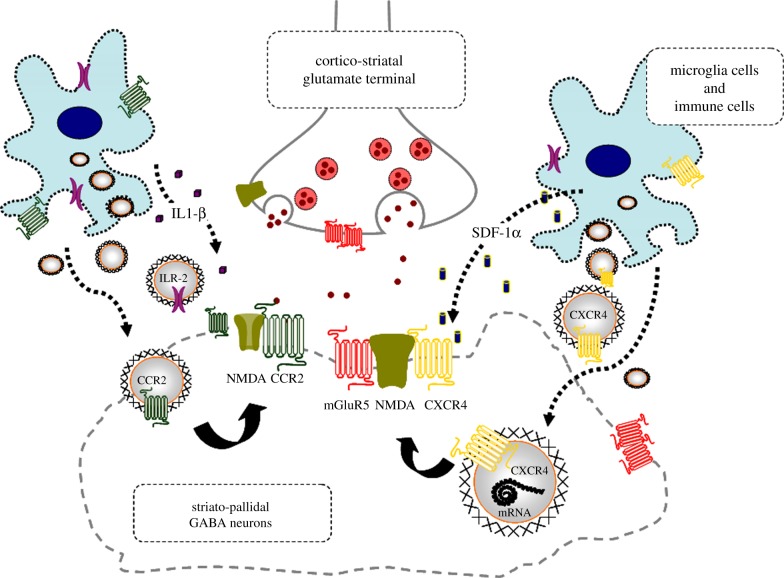
Figure 3.
Illustration of the potential chemokine and cytokine receptor transfer via ECV-VT from immune and microglial cells to neurons with NMDA receptors in mild inflammation. One mechanism is shown for how chemokine receptors CCR2 and CXCR4 and cytokine receptor interleukin-1 receptor, type II (ILR-2) including their mRNAs can produce schizophrenia-like symptoms in neuroinflammation. These receptors may be transferred via ECV-mediated VT from immune cells, activated microglia and/or astroglia to nerve cells containing NMDA receptors. Upon internalization the receptors CXCR4, CCR2 and ILR-2 can, according to the triplet puzzle theory (figure 2), form complexes with NMDA receptors as illustrated here. Through the development of novel allosteric receptor–receptor interactions in such heteroreceptor complexes NMDA signalling may become pathologically reduced, contributing to schizophrenia-like symptoms. (Online version in colour.)