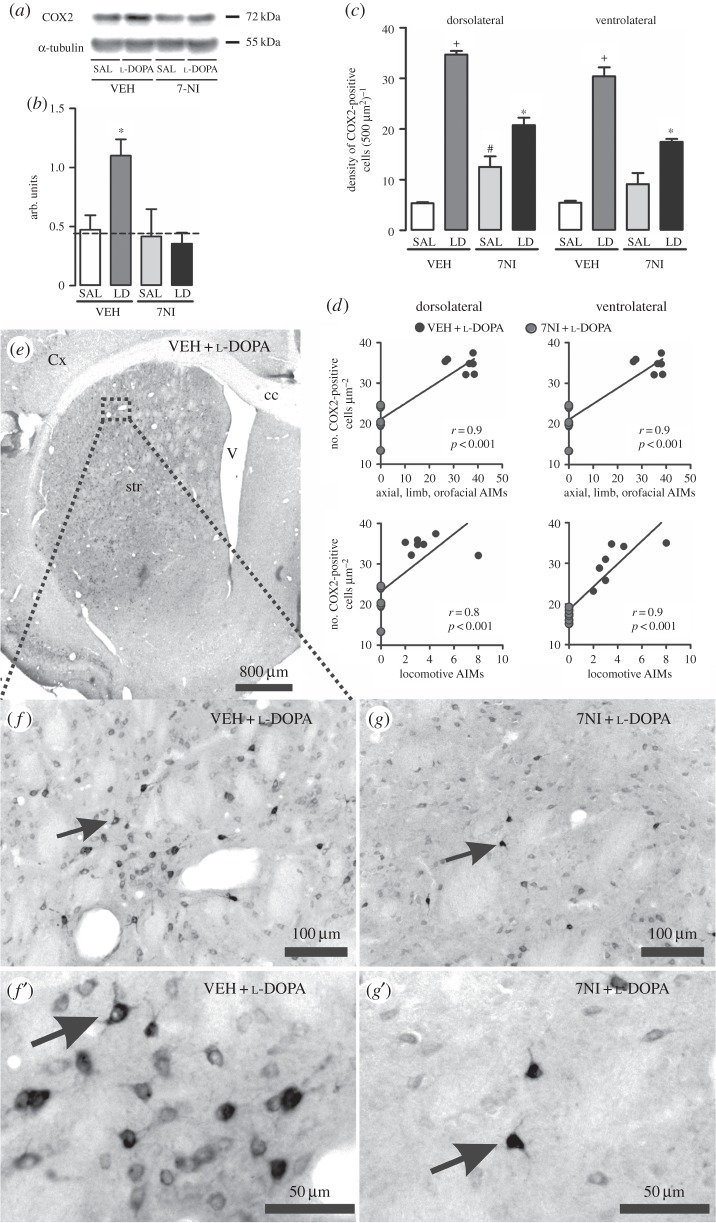
Figure 3.
Analysis of l-DOPA and 7NI effect on COX2 expression in the 6-OHDA-lesioned striatum of rats. (a) Representative Western blots of striatal COX2 (72 kDa) and α-tubulin (50 kDa, control). (b) Western blotting quantification of striatal protein extracts obtained from 6-OHDA-lesioned rats chronically treated with either VEH + SAL, 7NI + SAL, VEH + l-DOPA or 7NI + l-DOPA. Dashed line indicates the mean of COX2 expression in the contralateral side to the lesion. (c) Quantification of COX2-immunostaining cells in the 6-OHDA-lesioned striatum. VEH + l-DOPA treatment significantly increased COX2 protein expression in the dopamine-denervated striatum (p < 0.05 if compared with (*) all other groups, with (+) VEH + SAL and 7NI + SAL, with (#) VEH + SAL). (d) Graphics showing positive correlation between COX2 expression and abnormal involuntary movements induced by l-DOPA treatment in the hemi-Parkinsonian rats. (e,f and g) Photomicrographs showing COX2-immunopositive neurons in the dopamine-depleted striatum of VEH + l-DOPA (e,f and f’) and 7NI + l-DOPA (g and g’)-treated rats. (f’ and g’) show high magnifications of a COX2 neuron. Arrows indicate an example of a COX2-positive cell. AIMs, abnormal involuntary movements; LD, l-DOPA; 7NI, 7-nitroindazole; SAL, saline; VEH, vehicle; cc, corpus callosum; Cx, cortex; str, striatum; V, ventricle.