Figure 5.
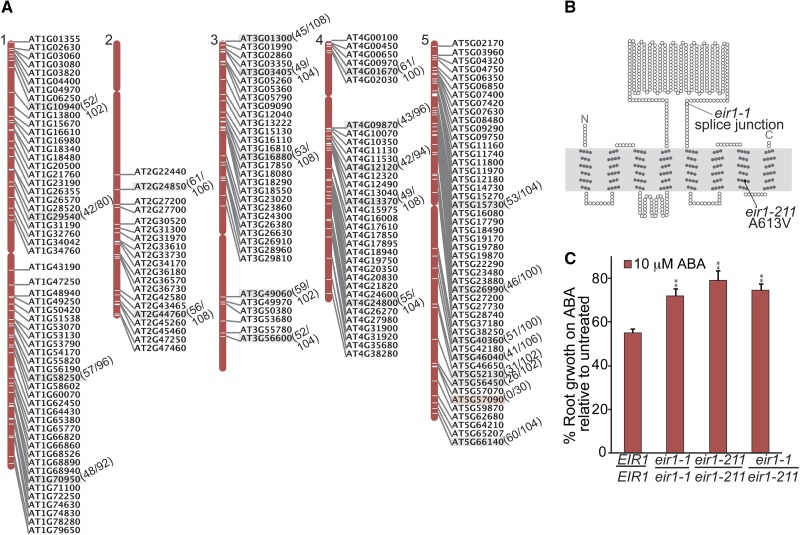
Whole genome sequencing of AR211 reveals a new allele of eir1. (A) Map positions of homozygous EMS-caused mutations identified in AR211. Genomic DNA from pooled M4 seedlings was sequenced and examined for G/C to A/T transitions typically associated with EMS mutagenesis in splice sites and coding sequences (see Table S3 for list of mutations identified). Approximate map positions of the identified mutations are shown to the right of each chromosome. PCR-based markers (Table S2) were designed for a subset of identified mutations and used to localize the AR211 causative mutation near At5g57090 with 0/30 recombination events in a population of AR211 backcrossed lines. Recombination events in examined backcrossed lines are listed to the right of gene names for each PCR-based marker. (B) Examination of EIR1/PIN2 in AR211 revealed a C-to-T mutation in the eighth exon causing an Ala613-to-Val mutation. (C) eir1-211 is allelic to eir1-1. Complementation test showing mean normalized primary root lengths (±SE; n = 15) of Col-0 wild-type (EIR1/EIR1), eir1-1/eir1-1, eir1-211/eir1-211, and eir1-1/eir1-211 seedlings grown under yellow-filtered light at 22° for 4 d on unsupplemented medium, followed by 4 d on medium supplemented with 10 µM ABA compared to mock-treated (ethanol) seedlings. Asterisks indicate that the mutant normalized root lengths were significantly longer than wild-type normalized root lengths on ABA (**P ≤ 0.001) in two-tailed t tests assuming unequal variance.