Fig. 2.
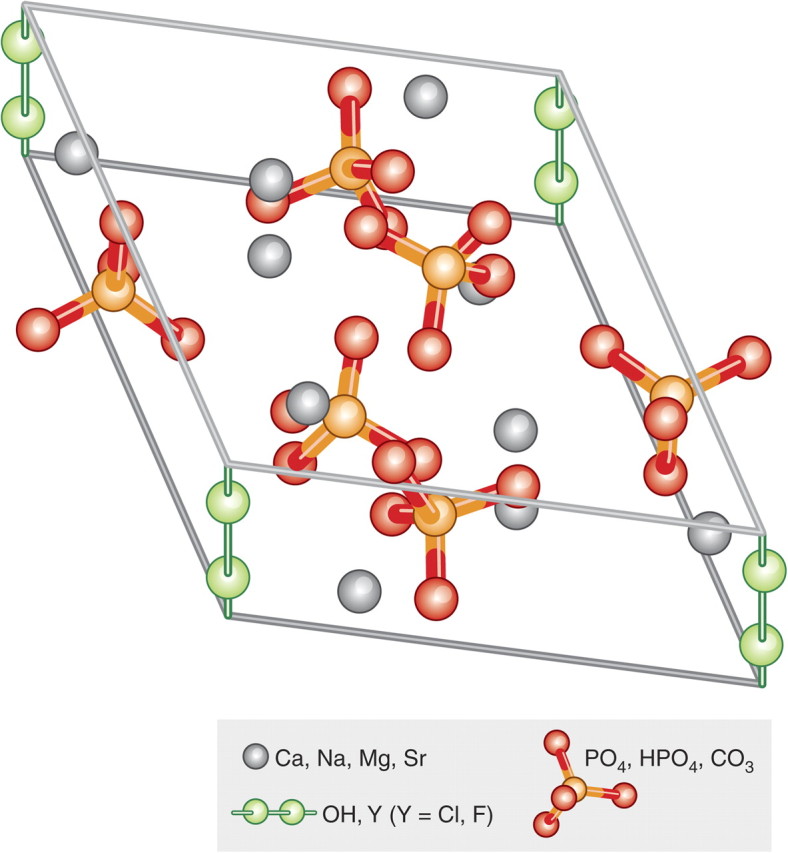
Hydroxyapatite crystal unit. Enamel apatite contains the lowest concentrations of carbonate and magnesium ions, and is rich in fluoride F. Dentin and bone have the highest levels of carbonate and magnesium ions, but have low fluoride content. Fluoride decreases solubility and increases chemical stability, carbonate, chloride and especially magnesium all increase solubility of the otherwise very insoluble mineral. Chemically the mineral comprises a highly substituted carbonated calcium hydroxyapatite (HAP). In the absence of exact compositional analysis the biogenic forms of this mineral are collectively alluded to as “bioapatite”. Ca, calcium; Na, sodium; Mg, magnesium; Sr, strontium; OH, hydroxide; Cl, chloride; F, fluoride; PO4, HPO4, phosphate; CO3, carbonate.
