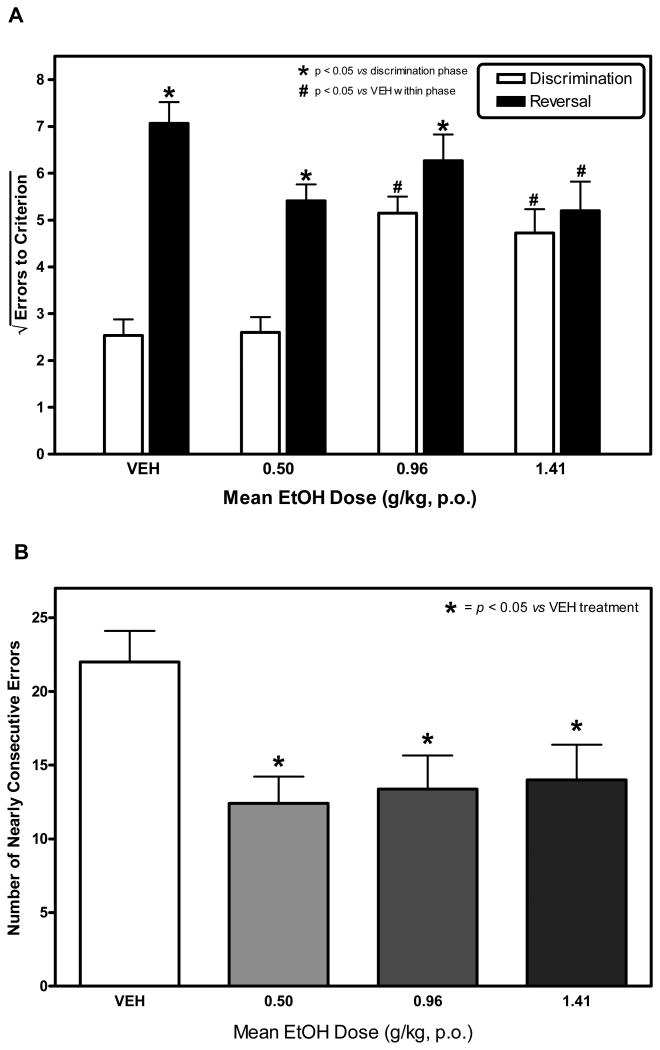
Figure 2.
A and B. The Influence of Acute Ethanol on Discrimination and Reversal Learning. In these trials, both discrimination and reversal learning took place within 90 minutes of ethanol consumption. Under these conditions, the effect of ethanol on errors-to-criterion (ETC) was dependent upon whether the monkey was engaged in discrimination or reversal learning. Ethanol increased ETC during discrimination learning and reduced ETC in reversal learning in a dose-related fashion (Fig 2A). As such, ethanol abolished the reversal effect commonly observed during reversal learning. At each dose tested, ethanol also reliably reduced perseverance as indexed by NCE (Figure 2B).