Figure 1.
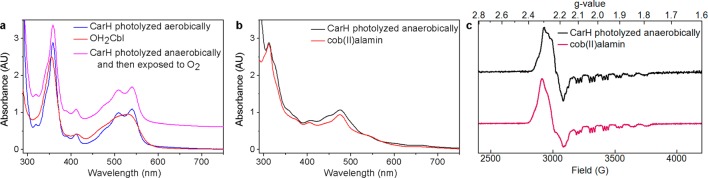
Fate of CarH cobalamin after photolysis. (a) The UV–vis spectrum of aerobically photolyzed CarH-bound AdoCbl (blue) has characteristic features of six-coordinate cob(III). The spectrum of OH2Cbl is shown as a comparison (red). In addition, the spectrum of anaerobically photolyzed CarH after exposure to molecular oxygen (pink, spectrum shifted by 0.6 AU) is identical to that of aerobically photolyzed CarH. (b) The UV–vis spectrum of anaerobically photolyzed CarH-bound AdoCbl (black) has characteristic features of cob(II). The spectrum of free cob(II) is shown as a comparison (red). (c) X-Band EPR spectrum of anaerobically photolyzed CarH (black), recorded at 77 K. The spectrum has features characteristic of cob(II). The spectrum of pure cob(II), generated from anaerobic photolysis of AdoCbl (red), is shown as a comparison.
