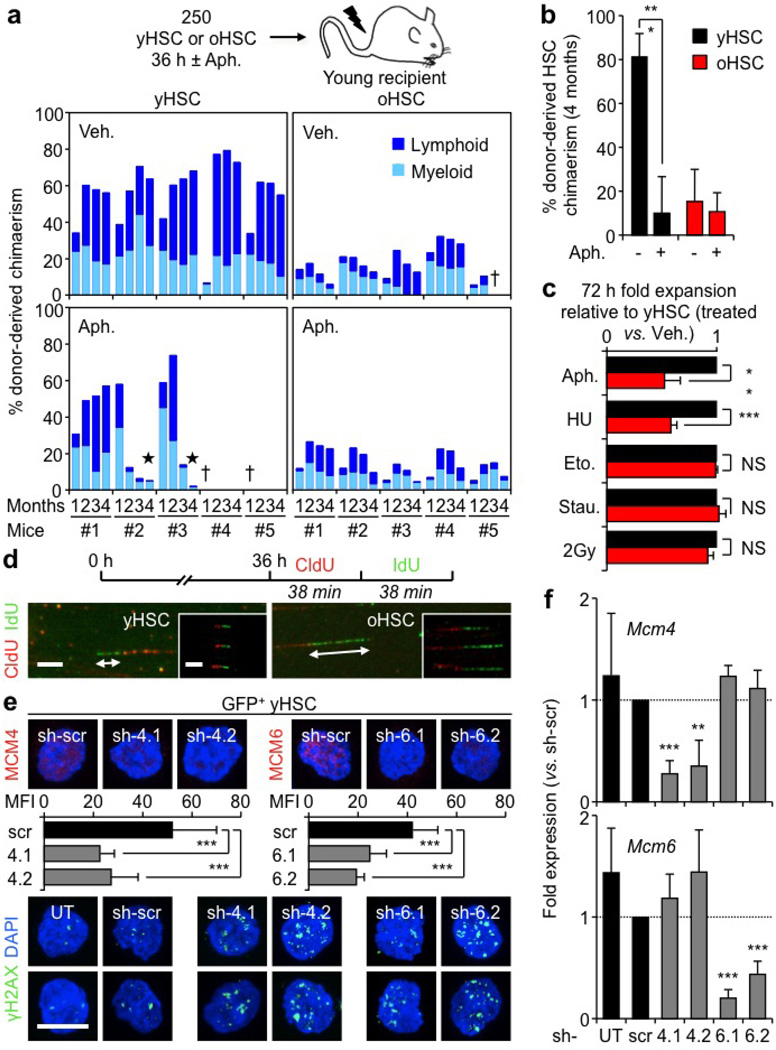
Extended Data Figure 7. Consequences of replication stress and decreased Mcm expression for HSC function.
a, Effect of replication stress on the reconstitution ability of young and old HSCs. HSCs were isolated from C57BL/6-CD45.2 donor mice, treated with aphidicolin (Aph; 50 ng ml−1) or vehicle (Veh; DMSO) for 36 h in vitro and transplanted (250 HSCs per mouse) into lethally irradiated young C57BL/6-CD45.1 recipients (n = 5 mice per cell type) together with 300,000 Sca1-depleted CD45.1 helper bone marrow cells. The percentage of donor-derived chimaerism and myeloid (light blue) versus lymphoid (dark blue) reconstitution in the peripheral blood was assessed by flow cytometry at the indicated months post-transplantation. Black star indicates bone marrow failure, dagger indicates animal mortality. b, Donor-derived chimaerism in the HSC compartment of the surviving mice at 4 months post-transplantation (n = 3–5). c, Differential killing of young and old HSCs after 72 h treatment. Eto, etoposide (0.25 µM); HU, hydroxyurea (100 µM); Stau, staurosporine (5 nM). Results are normalized for vehicle-treated cells and expressed as fold change compared with young HSCs (set to 1). d, Additional images of CldU/IdU-labelled stretched DNA fibres from replicating young and old HSCs. e, f, Effect of lentiviral-mediated knockdown of Mcm4 and Mcm6 on young HSCs (n = 3): e, additional images for MCM4 and MCM6 protein levels (with MFI quantification) and γH2AX foci; f, qRT–PCR analyses of Mcm4 and Mcm6 expression levels. Transduced GFP+ HSCs were re-isolated 48 h post-infection. Results are expressed as fold change compared with scrambled shRNA (scr)-infected HSCs. Two independent shRNA constructs are used per gene. UT, untransfected. Data are means ± s.d. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. NS, not significant. Scale bars, 1.5 µm insert, 3.5 µm (d); 10 µm (e).