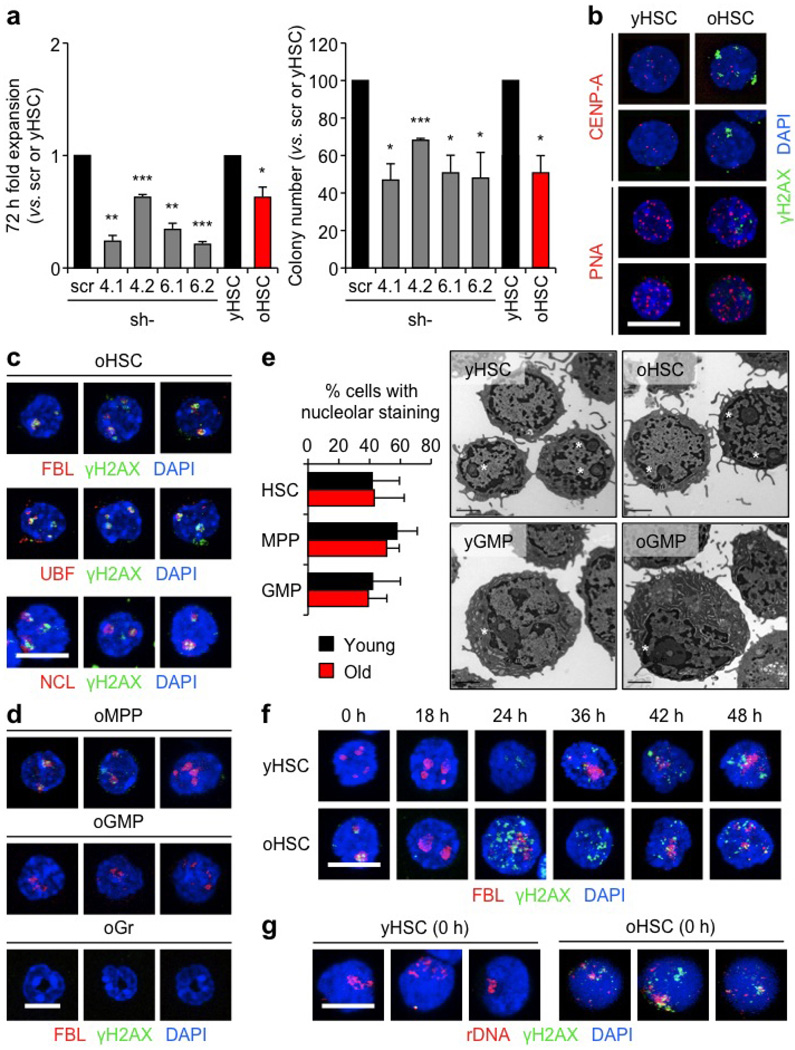
Extended Data Figure 8. Replication stress leads to persistence of nucleolar-associated γH2AX signals in quiescent old HSCs.
a, Functional effect of lentiviral knockdown of Mcm4 and Mcm6 on young HSCs, and direct comparison with old HSCs in liquid culture expansion (left) and methylcellulose (right). Transduced GFP+ HSCs were re-isolated 48 h post-infection. Results are expressed as fold change compared with scrambled shRNA (scr)-infected HSCs for transduced HSCs, and young HSCs for old HSCs. Two independent shRNA constructs are used per gene. b, Representative images of γH2AX and centromere marker (CENP-A) staining and immuno-FISH for γH2AX and telomeric PNA probe in young and old HSCs.
c, Additional images for γH2AX and nucleolar marker co-localization in old HSCs. d, Representative images of γH2AX and nucleolar marker colocalization in old MPPs, GMPs and granulocytes (Gr). e, Percentage of young and old cells with nucleolar staining (HSC: 445 and 464; MPP: 485 and 390; GMP: 179 and 223 cells scored, respectively) and representative electron microscopy images of young and old HSCs and GMPs. Data are means ± s.d. White asterisks indicate nucleoli. f, Representative images of γH2AX/FBL staining in cultured young and old HSCs. g, Additional images of immuno-FISH for γH2AX and rDNA probe in young and old HSCs. Scale bars, 10 µm (b, c, d, f, g); 2 µm (e).