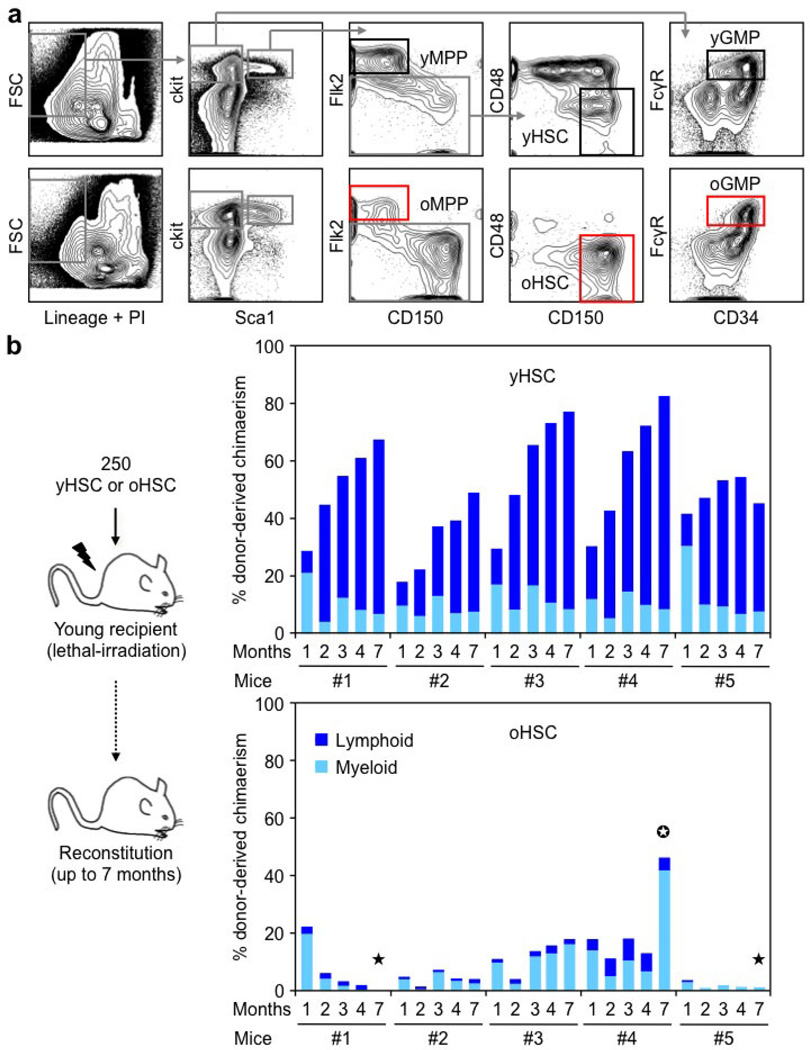
Extended Data Figure 1. Isolation strategy and functional impairment of old HSCs.
a, Gating strategy used to isolate HSCs (Lin−/Sca1+/c-Kit+/Flk2−/CD150+/CD48−), MPPs (Lin−/Sca1+/c-Kit+/Flk2+) and GMPs (Lin−/Sca1−/c-Kit+/FcγR+/CD34+) from the bone marrow of young (6–12 weeks) and old (22–30 months) C57BL/6 mice. o, old; y, young. b, Reconstitution ability of young and old HSCs. HSCs were isolated from C57BL/6-CD45.2 donor mice, and transplanted (250 HSCs per mouse) into lethally irradiated young C57BL/6-CD45.1 recipients (n = 5 mice per cell type) together with 300,000 Sca1-depleted CD45.1 helper bone marrow cells. The percentage of donor-derived chimaerism and myeloid (light blue) versus lymphoid (dark blue) reconstitution in the peripheral blood was assessed by flow cytometry at the indicated months post-transplantation. Stars indicate phenotypes resembling age-related blood disorders: black, bone marrow failure; white, myeloproliferative neoplasm.