Fig. 12.
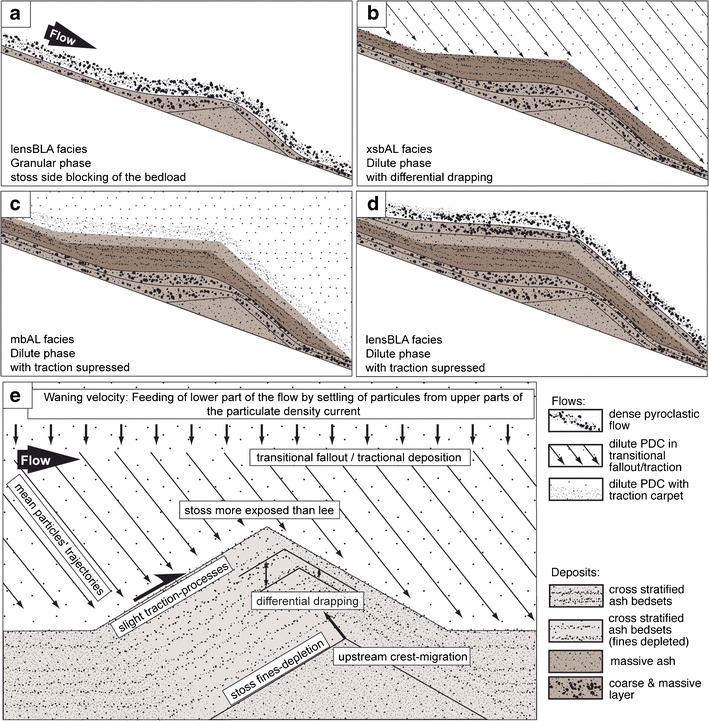
Interpretative sketch of a, b, c, and d, the formation of elongate DBs by successive flows, and e: regressive climbing dune. Currents are represented with grains only, deposits with grains, and background colors. a Granular phases deposit lensmBLA layers; b dilute phase deposits xsbAL bedset; c dilute phase with traction suppressed by high basal concentration deposits mbAL bedset; d granular phase deposits lensmBLA layer. e Regressive climbing dunes are formed by the differential exposition between stoss and lee faces, in turns driven by the mean particle trajectories that have a fall and a lateral component, together with little traction after initial landing
