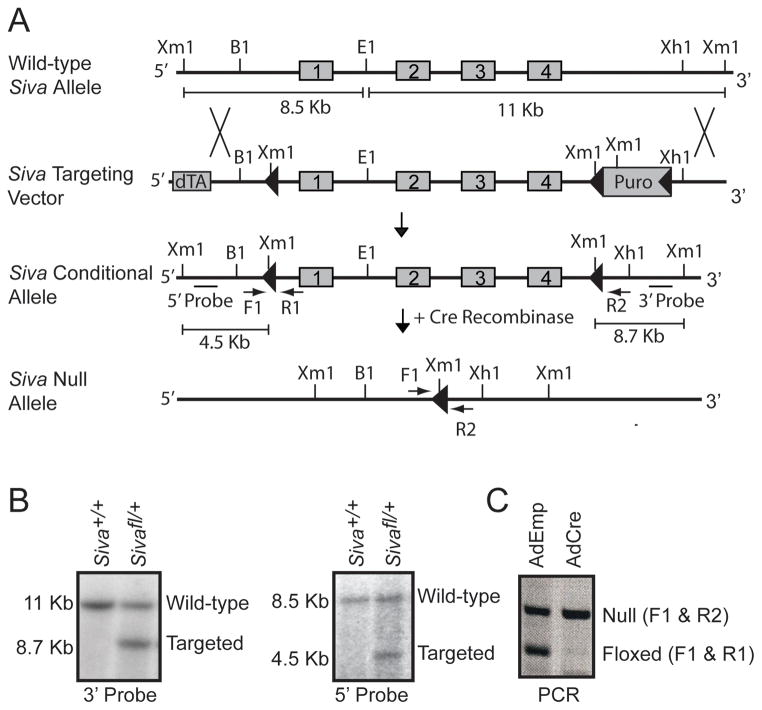
Figure 1. Generation of Siva Conditional Knockout Mice.
A) Targeting scheme for generating Siva conditional knockout mice. The Siva-targeting vector contains a positive selection marker (Puromycin cassette (Puro)) flanked by loxP sites (triangles) and a negative selection marker (diphtheria toxin (dTA)). The four exons comprising the Siva locus (grey boxes) are flanked by LoxP and Lox-Puro-Lox sites on the 5′ and 3′ ends, respectively. The Puro cassette was removed in vivo by limited Cre expression, leaving a single 3′ LoxP site. Upon subsequent Cre recombinase expression, the Siva locus gets excised, resulting in a Siva null allele. These recombination events were detected by Southern blot analysis using Xmn1/EcoR1 restriction digests and subsequent probing with a 5′ or 3′ fragment external to the targeting vector. This leads to generation of fragments of different sizes in all cases, as shown. B1: BamH1, E1: EcoR1, Xm1: Xmn1, Xh1: Xho1 B) Southern blot analyses of mouse embryonic stem cells targeted at the Siva locus. Analyses of a wild-type (Siva+/+) and a targeted (Sivafl/+) ES cell clone are shown. DNA was digested with Xmn1/EcoR1. Left: Upon probing with the 3′ probe, the 11 Kb band indicates the wild-type allele and the 8.7 Kb band indicates the targeted conditional allele. Right: Upon probing with the 5′ probe, the 8.5 Kb band indicates the wild-type allele and the 4.5 Kb band indicates the targeted conditional allele. C) PCR analysis of recombined allele. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts generated from E13.5 Sivafl/− embryos (where fl denotes the conditional knockout allele) were infected either with Adenovirus expressing Cre (Ad-Cre) to excise the Siva floxed allele or with empty Adenovirus (Ad-Emp) as a control. Primers spanning the 5′ LoxP site (F1 and R1) or the remaining LoxP site after excision of the Siva locus (F1 and R2) were used. The absence of the floxed allele following Ad-Cre infection verifies the ability of Cre to fully excise the Siva locus.