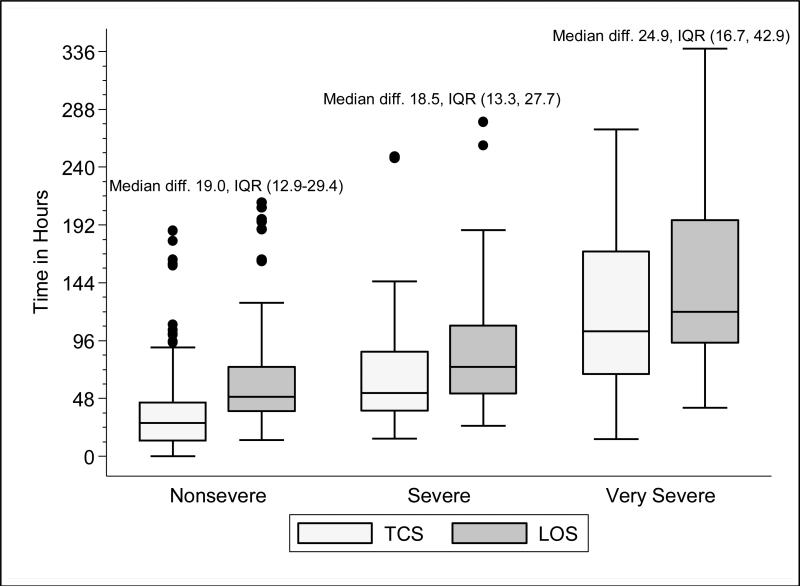
Figure 1A. Time to Clinical Stability (Respiratory Rate and Supplemental Oxygen Need) and Length of Stay According to Disease Severity Among Children Hospitalized with Pneumonia.
Time to clinical stability (TCS measure incorporating respiratory rate and supplemental oxygen need) and length of stay (LOS) according to pneumonia disease severity. The median absolute difference between LOS and time to clinical stability along with interquartile range values by disease severity is also presented. The ordinal severity scale categorized children into three mutually-exclusive groups as follows: non-severe, severe, and very severe. Box and whisker plots represent the median, interquartile range, and 1.5 times the interquartile range. P-value <0.01 for non-parametric test of trend comparing time to stability according to disease severity. Abbreviations: diff., absolute difference; IQR, interquartile range; TCS, time to clinical stability; LOS, length of stay