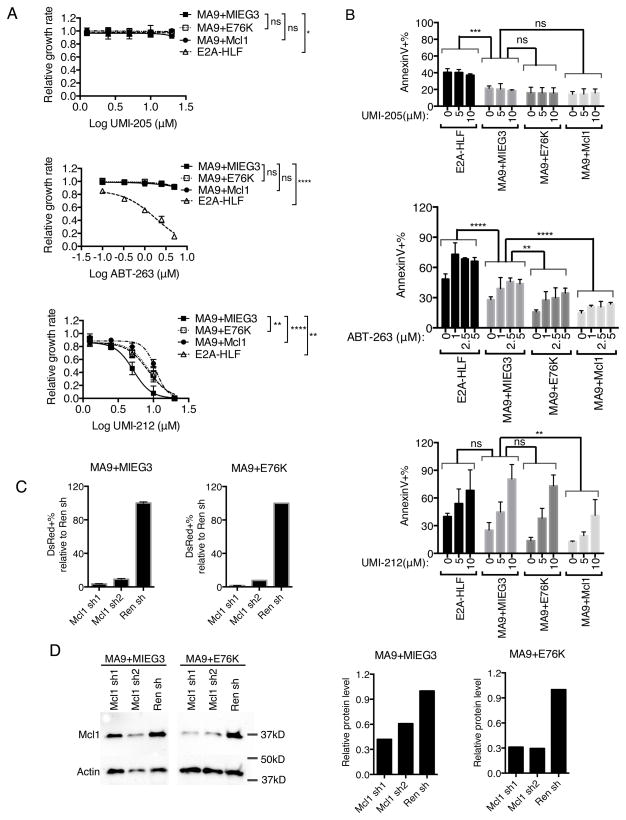
Figure 6.
Shp2E76K desensitizes MLL-AF9 cells to Mcl1 inhibition. (A) Growth rate of E2A-HLF, MA9+MIEG3, MA9+E76K, MA9+Mcl1 cells was determined after treatment with DMSO carrier or ABT-263, UMI-205, UMI-212 chemical inhibitors. Average growth rates from biological duplicate experiments are normalized to DMSO control and shown with standard deviation after 48 hours of chemical treatment and plotted against concentration with a fitted sigmoidal curve. Data indicates ABT-263 preferentially inhibits E2A-HLF while UMI-212 mediated Mcl1 inhibition preferentially inhibits MLL-AF9 cell growth, which is mitigated by Shp2E76K. (2-away Anova, * p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001) (B) Quantified flow cytometry data from cells co-stained with AnnexinV and DAPI. Data shows increased apoptosis with chemical inhibition of Mcl1 or Bcl2/Bcl-xL which is lessoned by Shp2E76K. Statistical analysis was performed by 2-way Anova (** p<0.01, *** p<0.001; **** p<0.0001, ns= Not Significant) (C) MA9+MIEG3, MA9+E76K cells were transduced with shRNA retroviruses targeting Mcl1 and selected with Hygromycin for 1 week before performing a competitive growth assay in the presence of Doxycycline to induce shRNA expression. Average dsRed+ population percentages with standard deviation were determined by flow cytometry after 1 day. Data is plotted relative to cells transduced with control shRNA targeting renilla (Ren sh). (D) Mcl1 knockdown was verified by western blot and the relative protein level was quantified with image lab software (BioRad).