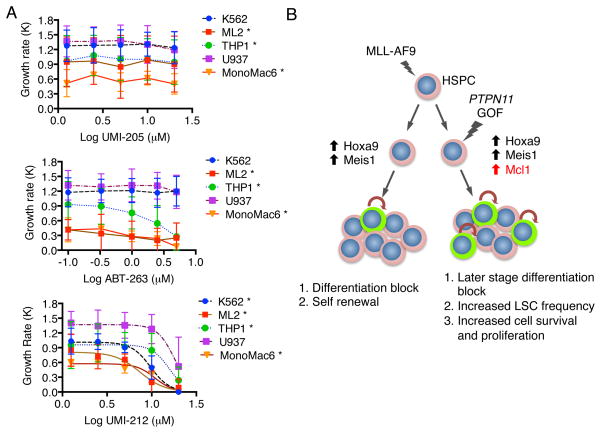
Figure 7.
Human leukemia cell lines with activated SHP2 mutations show resistance to Mcl1 inhibitors. (A) The growth rate of K562, U937, THP-1, Monomac6 and ML2 cells was determined following culture with UMI-205 (negative control), ABT-263 (Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor), and UMI-212 (Mcl1 inhibitor) and plotted against concentration with a fitted sigmoidal curve. Averaged data with standard deviation are shown for biological duplicate experiments normalized to DMSO treatment indicates the Shp2 mutation in U937 cells leads to greater resistance to Mcl1 inhibition. * indicates statistical significance (p<0.05) between the indicated cell line and the U937 cell line (2-way ANOVA) (B) Model of mechanistic cooperation between MLL-AF9 and Shp2E76K. A pre-leukemic clone containing an MLL-AF9 fusion protein displays blocked differentiation and increased self-renewal through upregulation of Hoxa9 and Meis1. A second genetic lesion involving a gain of function (GOF) mutation to PTPN11 leads to increased expression of Mcl1 which increases leukemic stem cell (green) frequency and cell survival.