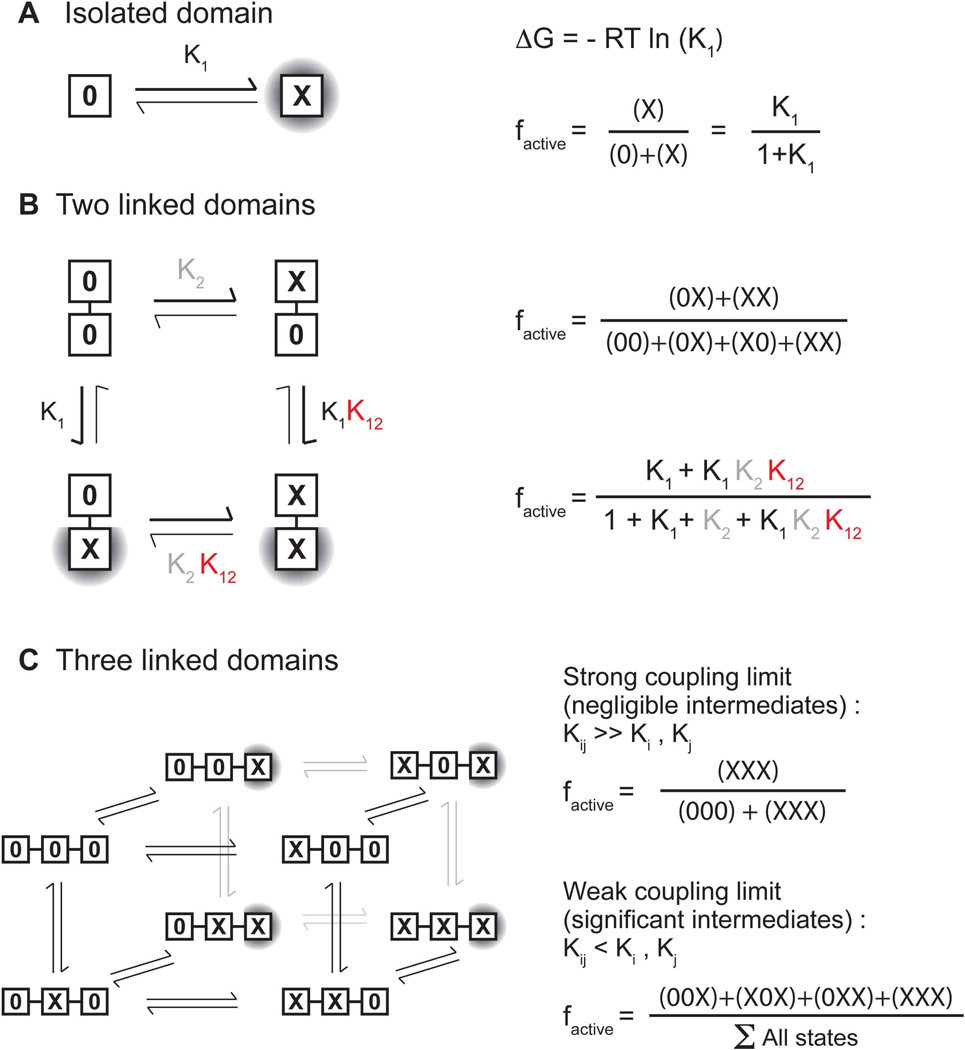
Figure 9. A thermodynamic framework for signal transduction.
A) shows a single domain that has two states, an active state (X) or an inactive state (0). The population of the active state is directly related to the energy difference between these two states i.e. the equilibrium constant. B) shows two thermodynamically coupled domains. The fraction of the active state depends on two equilibrium constants and a coupling energy. C) extends this formalism to three linked domains. In the limit of rigid, all-or-nothing coupling between the domains, the system reduces to a 2 state system but in the limit of weak coupling, multiple intermediates contribute to the active population.