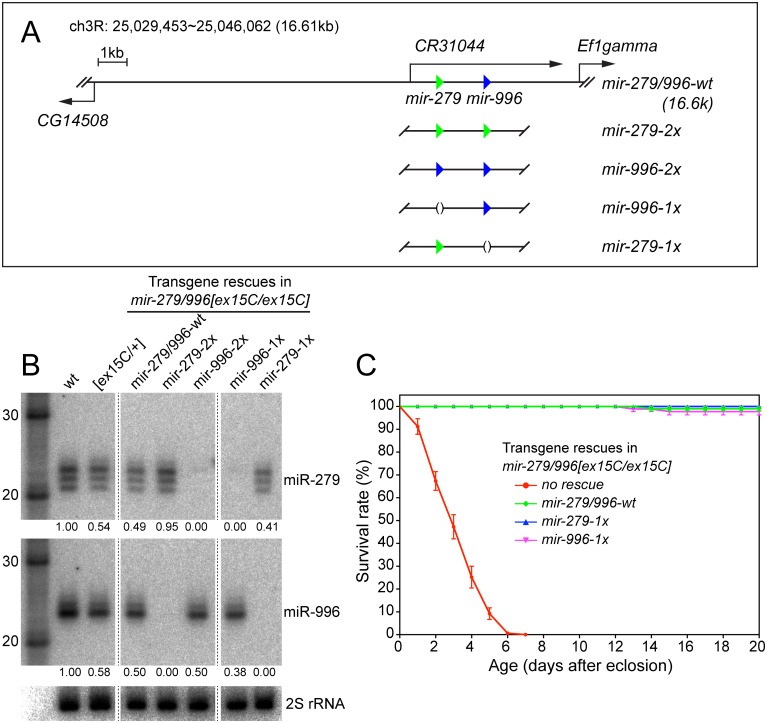
Fig 3. Modified genomic transgenes to assess individual miR-279/996 functions.
(A) In the 16.6kb mir-279/996 rescue transgene, the 5' end extends to cover a portion of the upstream CG14508 gene and 3' end extends into the downstream Ef1gamma gene. Green and blue triangles represent mir-279 and mir-996 hairpins, respectively. The wildtype genomic fragment was modified to replace the mir-279 and mir-996 hairpins with either a deletion or the non-cognate miRNA. (B) Northern blots verify the expression of miR-279 and miR-996 from different genomic transgenes that were introduced into mir-279/996[ex15C] double mutant homozygous animals. RNA samples were extracted from whole flies carrying one copy of individual transgenes. Intensities of miR-279 and miR-996 expression were quantified by normalization to homozygous wild type and marked below each lane. mir-996-2x expressed only comparable amount of miR-996 as mir-279/996-wt and mir-996-1x transgenes. (C) Rescue of the lifespan defect in mir-279/996[ex15C] double mutants by 16.6kb transgenes. The mir-279/996[ex15C] data shown here are the same as plotted in Fig 1C. For each genotype, 100 flies including equal number of males and females were assayed; error bars represent SEM.