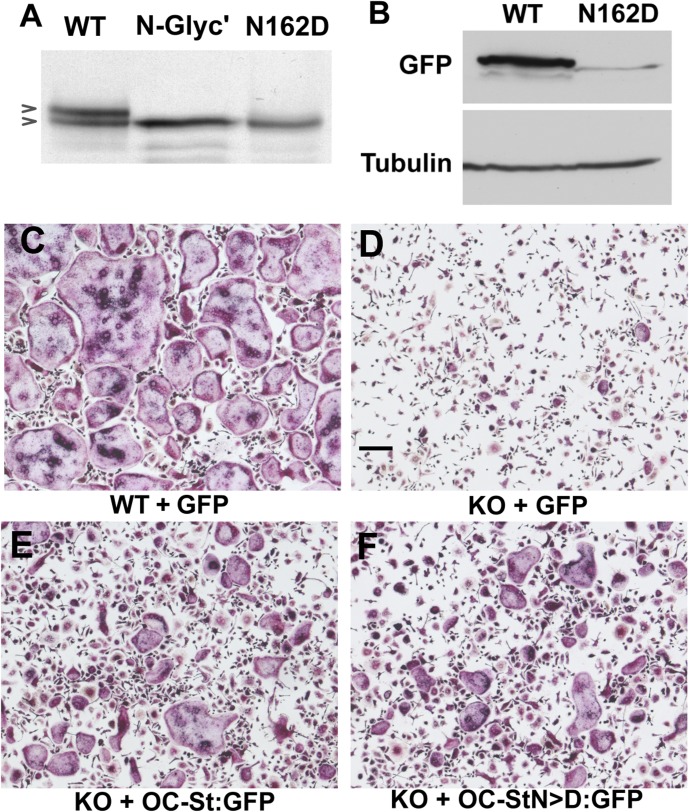
Fig 8. Glycosylation of OC-STAMP.
A. HEK293 cells were transfected with V5-tagged wild type (WT) OC-STAMP or glycosylation-deficient (N162D) OC-STAMP. Wild type-transfected cell extracts were either untreated or digested with N-glycanase (N-Glyc’). Extracts were blotted and probed with anti-V5 antibody. Arrowheads indicate 2 bands, an upper, glycosylated form approximately 3kDa higher than the lower band at 50 kDa. Both N-glycanase-treated and the N >D mutation show only the low molecular weight form. Some of the overexpressed WT protein escapes glycosylation, giving 2 bands. B. BMMC from OCSt-KO mice were transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding wild type (WT) or (N162D) OC-STAMP fused to GFP. Cells were cultured for 6 days in RANKL, and extracts were blotted and probed with anti-GFP (upper panel) or anti-α-tubulin (lower panel). The glycosylated WT OC-STAMP appears to have much greater stability. C-F. TRAP enzyme cytochemistry. Wild type (WT) or OCSt-KO BMMCs were differentiated with RANKL for 6 days in 96-well plates. They were transduced with either GFP (C, D), OC-STAMP-GFP fusion protein (OCSt:GFP; E), or OC-STAMP-GFP fusion carrying the N162 mutation D (OC-StN>D; F). Fusion was rescued in the knockout cells by either the glycosylated or the non-glycosylated form of OC-STAMP. Bar in D = 200 μm.