FIG 1.
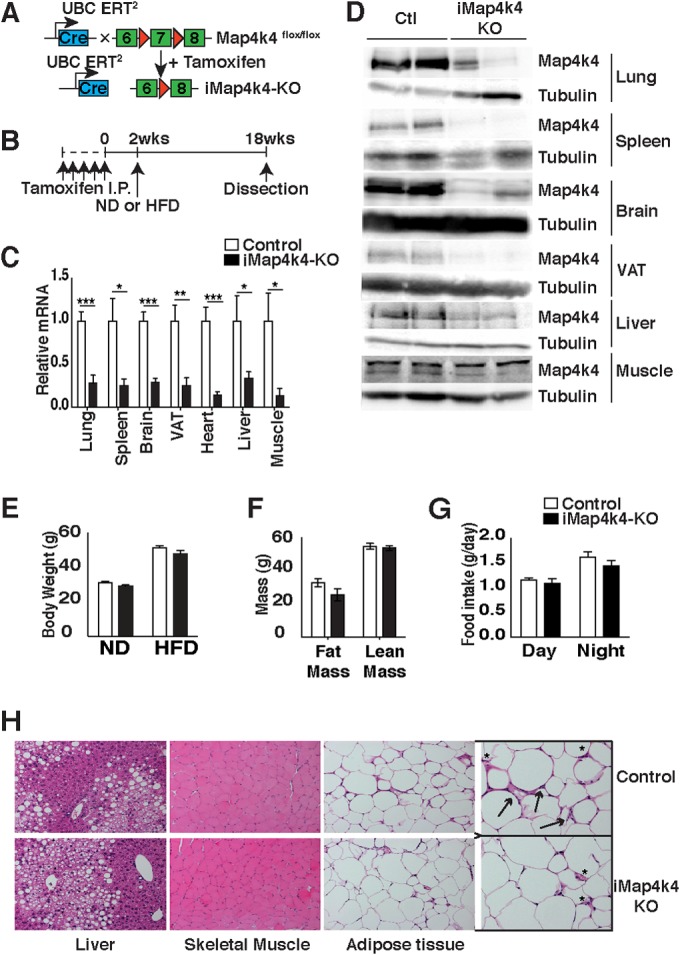
Characterization of tamoxifen-inducible whole-body iMap4k4-KO mice. (A) Schematic of alleles and transgenes used to inactivate Map4k4 systemically in adult tissues using tamoxifen. (B) Schematic of experimental design. Both control (Map4k4flox/flox) and iMap4k4 (Map4k4flox/flox-UBC-cre ERT2) mice were injected with tamoxifen as detailed in Materials and Methods to produce iMap4k4-KO mice. (C and D) Analysis was performed 18 weeks after first tamoxifen injection. (C) Map4k4 mRNA expression (n = 6 to 10). (D) Representative Map4k4 protein immunoblot with tubulin as the loading control (Ctl) (n = 6). (E to H) Control and iMap4k4-KO mice were fed a normal chow diet (ND) or a high-fat diet (HFD) for 16 weeks starting 2 weeks after the 1st tamoxifen injection. (E) Body weight (n = 16). (F) Fat and lean mass analysis in HFD-fed mice (n = 4 to 6). (G) Food intake in mice fed an HFD (n = 4 to 6). (H) Representative liver, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue histology of HFD-fed mice stained for H&E (n = 6). Arrows indicate crown-like-structures, and asterisks sites indicate of inflammation. Data represent means ± SEM (*, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001).
