FIG 4.
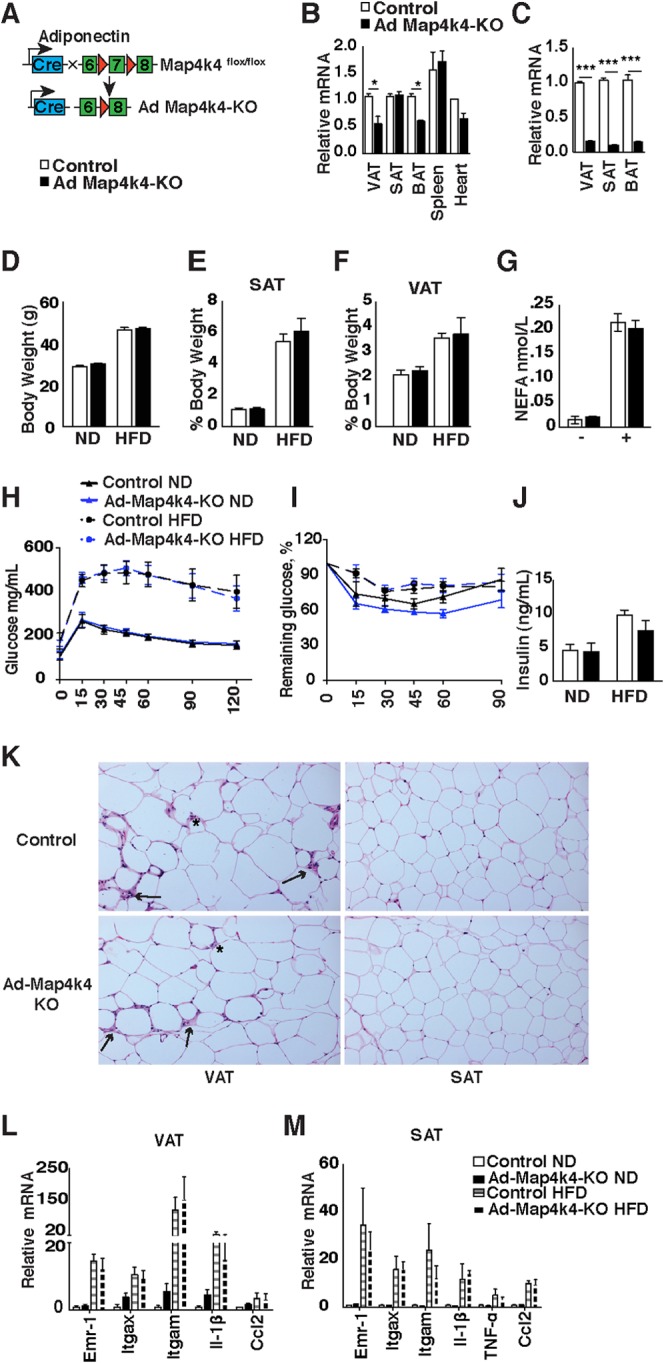
Adipose-specific Map4k4 deletion in mice does not alter systemic glucose tolerance or insulin responsiveness. (A) Schematic of alleles and transgenes used to inactivate Map4k4 in the adipose using adiponectin-cre transgene. (B) Relative levels of Map4k4 mRNA expression in adipose tissues (visceral adipose tissue [VAT], subcutaneous adipose tissue [SAT], and brown adipose tissue [BAT]), spleen, and heart (n = 4). (C) Relative levels of Map4k4 mRNA expression in isolated adipocytes from VAT, SAT, and BAT (n = 3). (D to M) Control and Ad-Map4k4-KO mice were fed an ND or an HFD for 16 weeks. (D) Body weight (n = 8 to 14). (E) SAT mass relative to body weight (n = 5). (F) VAT mass relative to body weight (n = 5). (G) NEFA levels in HFD-fed mice before and after 1 h CL 316,243 i.p. injection (n = 5). (H) GTT (n = 10 to 15). (I) ITT (n = 10 to 15). (J) Fasting insulin levels (n = 5 to 6). (K) Representative histology of VAT and SAT in HFD-fed mice. Slides were stained with H&E (n = 10). Arrows indicate crown-like-structures, and asterisks indicate sites of inflammation. (L and M) Relative mRNA levels of various inflammatory genes assessed in VAT (L) (n = 6 to 8) and SAT (M) (n = 6 to 8). Results are means ± SEM (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.0001).
