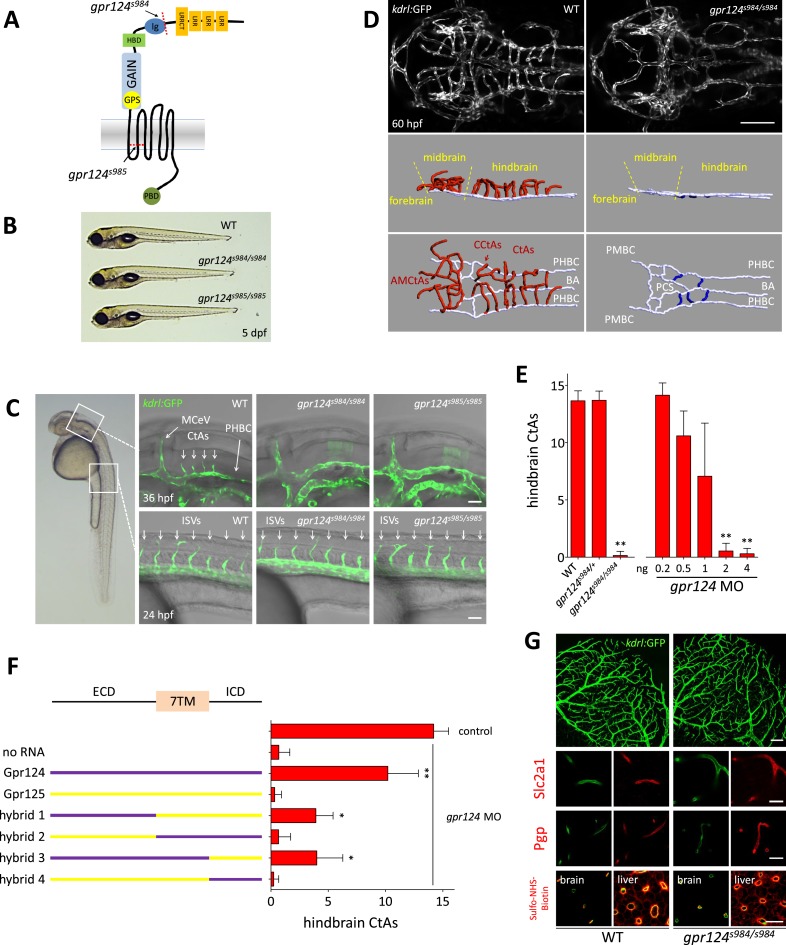
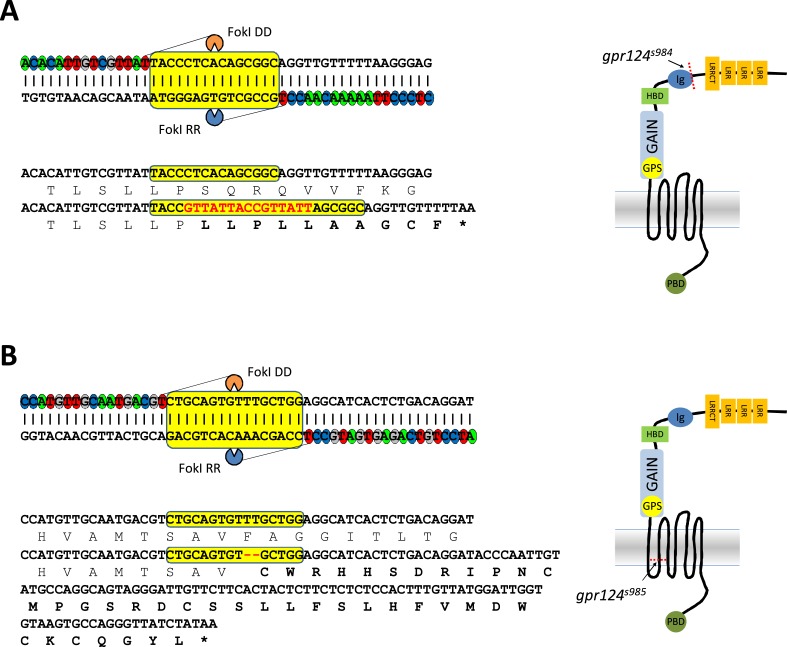
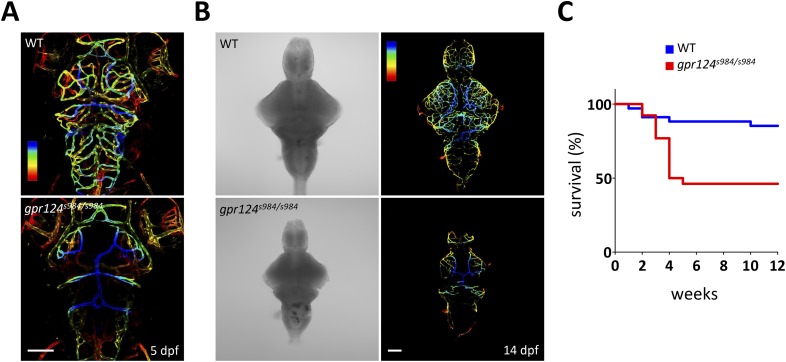
Figure 1. CNS vascular defects in gpr124 mutants.
(A) Schematic representation of Gpr124 structure and TALEN target site locations corresponding to gpr124s984 and gpr124s985 alleles. LRR: leucine-rich repeats; LRRCT: leucine-rich repeat C-terminal domain; Ig: Ig-like domain; HBD: hormone binding domain; GAIN: GPCR-autoproteolysis inducing domain; GPS: GPCR proteolysis site; PBD: PDZ binding domain. (B) Lateral views of wild-type, gpr124s984/s984 and gpr124s985/s985 larvae at 5 dpf. (C) Lateral views of wild-type, gpr124s984/s984 and gpr124s985/s985 Tg(kdrl:GFP) embryos at 36 hpf (hindbrain region, upper panels) and 24 hpf (trunk region, bottom panels). MCeV: middle cerebral vein. Scale bar, 50 µm. (D) Maximal intensity projection of a confocal z-stack of the cranial vasculature of Tg(kdrl:GFP) wild-type and gpr124s984/s984 embryos at 60 hpf in dorsal views (anterior to the left) and wire diagram of the brain vasculature in lateral (middle panels) and dorso-lateral (bottom panels) views. Red vessels in the 3D renderings represent the intra-cerebral central arteries (CtAs), blue vessels represent the extra-cerebral connections between the PHBC and BA lining the hindbrain ventrally, and gray vessels represent the perineural vessels (PHBC, PMBC, BA, and PCS) to which the central arteries connect in wild-type embryos. Scale bar, 100 μm. (E) Quantification of hindbrain CtAs upon Gpr124 depletion in 60 hpf embryos. (F) Quantification of hindbrain CtAs in control and gpr124 morphants at 60 hpf after injection at the one-cell stage of 100 pg RNA encoding the depicted receptors or Gpr124/Gpr125 hybrid receptors. (G) Vasculature of wild-type and gpr124 mutant adults. Single plane confocal image of the vascular network (upper panels: scale bar, 100 µm) and immunostaining for Slc2a1 and Pgp in sections through the optic tectum (middle panels: scale bars, 20 µm). Evaluation of the optic tectum and liver vessel permeability by fluorescent streptavidin labelling (red signal) 60 min after intracardial injection of sulfo-NHS-biotin in live animals (bottom panels; scale bar, 20 µm). In all panels, values represent means ± SD (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; Kruskal–Wallis test). Morpholino and RNA injections were performed as described in ‘Methods’.