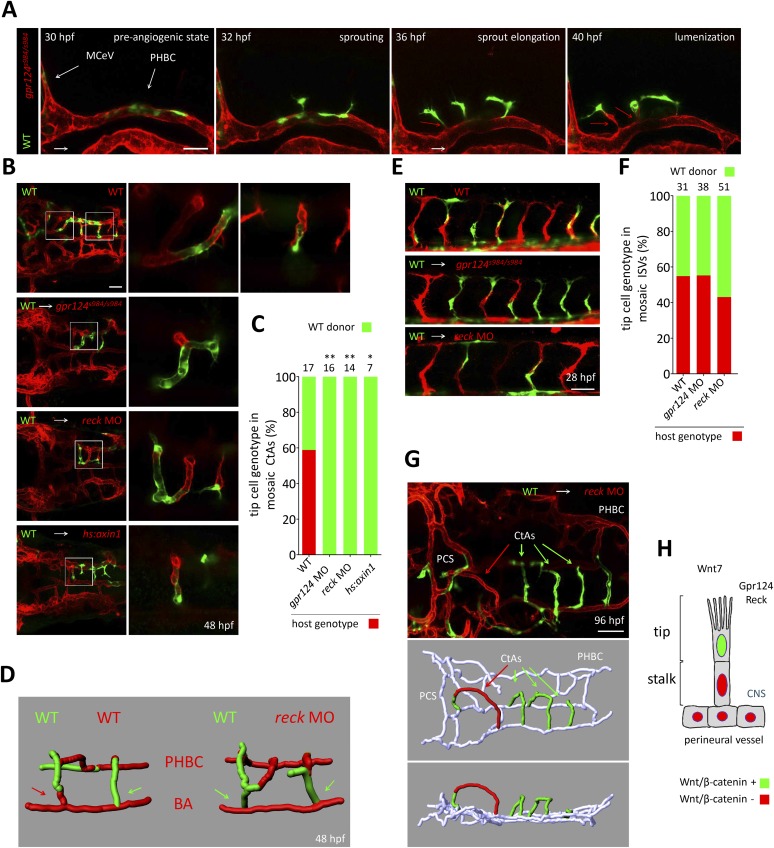
Figure 7. Tip cell-specific requirement for Gpr124 and Reck-controlled Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
(A) Stills from Video 8 recording sprouting angiogenesis from a mosaic PHBC obtained by blastula-stage transplantation. Green kdrl:GFP+ endothelial cells derive from a wild-type donor embryo, red kdrl:ras-mCherry+ endothelial cells are from the gpr124s984/s984 host. (B) Dorsal views of 48 hpf mosaic cranial vasculatures of the indicated genotypes. Right panels are high magnification views of a confocal z-stack of relevant depth illustrating intra-cerebral mosaic CtAs corresponding to the boxed areas in the left panels. (C) Contribution of cells of defined genotype to the tip cell position of mosaic CtAs after transplantation of wild-type Tg(kdrl:GFP) donor cells (green) into Tg(kdrl:ras-mCherry) host blastulae of the indicated genotype (red). Number of mosaic vessels analyzed is indicated above each bar. (D) 3D Imaris (Bitplane) reconstruction of representative hindbrain mosaic vascular networks. Arrows point to the cells connecting with the BA, after leading the CtA as tip cells. (E) Lateral views of the trunk region after transplantation of Tg(kdrl:GFP) wild-type donor cells into Tg(kdrl:ras-mCherry) host blastulae of the indicated genotype. (F) Contribution of cells of defined genotype to the tip cell position of mosaic ISVs after transplantation of wild-type Tg(kdrl:GFP) donor cells (green) into Tg(kdrl:ras-mCherry) host blastulae of the indicated genotype (red). Number of mosaic vessels analyzed is indicated above each bar. (G) Dorsal view of the cranial vasculature and 3D Imaris (Bitplane) reconstruction of the brain vessels of a 96 hpf mosaic larva after transplantation of wild-type Tg(kdrl:GFP) donor cells into reck morphant Tg(kdrl:ras-mCherry) host blastula. (H) Cellular requirement for Wnt/β-catenin, Gpr124, and Reck during sprouting angiogenesis in the zebrafish CNS (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; exact Fisher test).