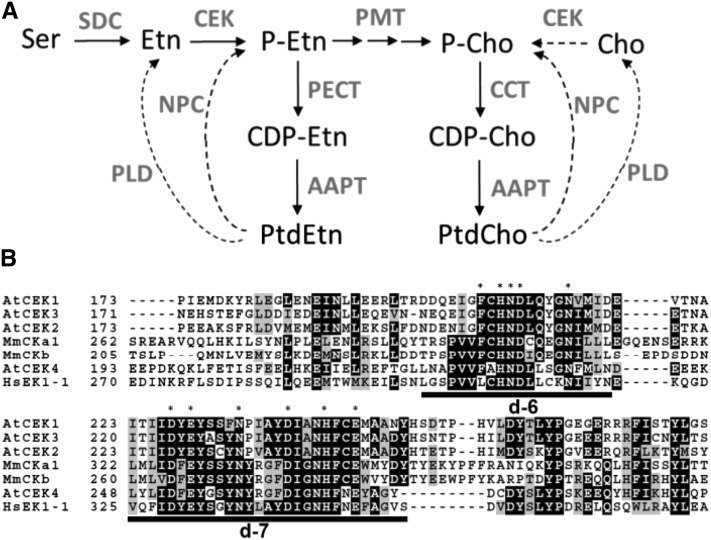
Figure 1.
The CEK Family in Arabidopsis.
(A) Proposed biosynthetic pathway of PtdCho and PtdEtn in Arabidopsis. Arrows indicate de novo biosynthesis, and dashed arrows indicate phospholipid hydrolysis pathways that provide phosphor-base compounds. Compounds are indicated in black letters and enzymes in gray. AAPT, aminoalcohol aminophosphotransferase; CCT, CTP:phosphorylcholine cytidylyltransferase; CDP-Cho, cytidine diphosphocholine; CDP-Etn, cytidine diphosphoethanolamine; Cho, choline; NPC, nonspecific phospholipase C; PECT, CTP:phosphorylethanolamine cytidylyltransferase; PLD, phospholipase D; SDC, serine decarboxylase.
(B) Amino acid sequence alignment of putative catalytic motifs in CEKs. Asterisks indicate highly conserved amino acid residues, and catalytic domains d-6 (Brenner’s phosphotransferase motif) and d-7 (putative CEK motif) defined by (Aoyama et al. 2004) are underlined. Hs, Homo sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus.