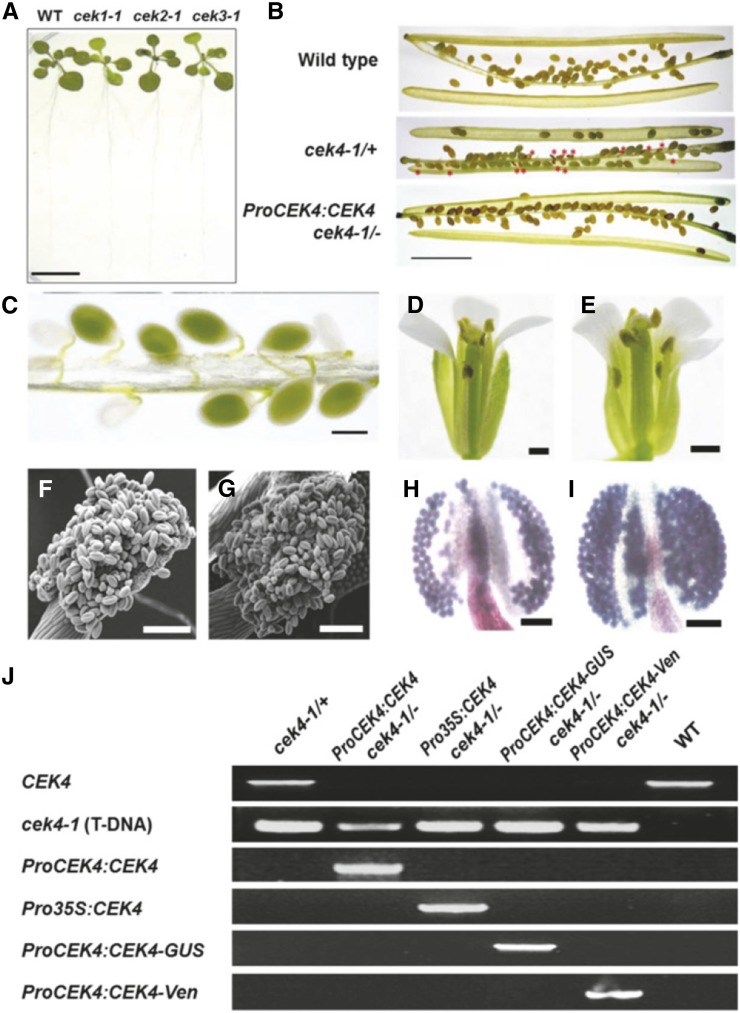
Figure 4.
Phenotype of cek Mutants.
(A) The phenotype of 14-d-old homozygous cek1-1, cek2-1, and cek3-1 mutants and the wild type. Bar = 10 mm.
(B) Siliques of the wild type, cek4-1/+ (producing wrinkled seeds; red asterisks), and ProCEK4:CEK4 cek4-1/- (producing normal seeds). Bar = 5 mm.
(C) Developing seeds (green or white) in a silique of cek4-1/+. Bar = 500 μm.
(D) and (E) Flower of the wild type (D) and cek4-1/+ (E). One petal was removed for observation. Bars = 1 mm.
(F) and (G) Scanning electron microscopy image of wild-type (F) and cek4-1/+ (G) pollen. Bars = 100 μm.
(H) and (I) Alexander’s staining of wild-type (H) and cek4-1/+ (I) pollen. Bars = 100 μm.
(J) PCR-based genotyping of complemented cek4-1/- plants by ProCEK4:CEK4, ProCEK4:CEK4-GUS, or ProCEK4:CEK4-Ven. See Supplemental Figure 3 for annealing positions and Supplemental Table 10 for sequences of the primers used.