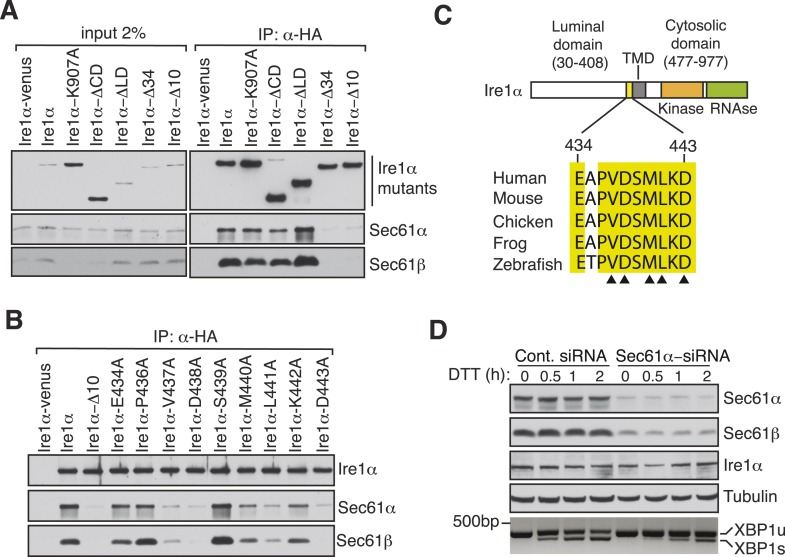
Figure 2. Key residues in Ire1α important for the interaction with the Sec61 translocon.
(A) The cell lysates of the indicated versions of HA-tagged Ire1α were IP with anti-HA antibodies, eluted with sample buffer and analyzed by IB. Ire1α–venus served as a control. The mutation K907 to A907 impairs the RNase activity of Ire1α (Tirasophon et al., 2000). Deletion of the Ire1α cytosolic domain from amino acid 477 to 977 or luminal domain from amino acid 30 to 408 is labeled as ΔCD or ΔLD (Volmer et al., 2013), respectively. Ire1α Δ34 carry a deletion from amino acid 409 to 443 and Ire1α Δ10 lacks amino acids 434 to 443. (B) The indicated Ire1α mutants were analyzed as described in panel A. (C) Comparison of the sequences of the 10 amino acid region of Ire1α in vertebrates. Triangle depicts amino acid residues of Ire1α in which alanine scanning mutations disrupt binding to the Sec61 translocon. (D) HeLa cells were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA targeting Sec61α. After 48 hr of transfection, cells were transfected again with siRNA which was followed by transfection with FLAG-tagged XBP1u. 96 hr after the first transfection, cells were treated with 10 mM DTT for the indicated time periods. Total proteins and RNA were isolated from Trizol harvested cells and analyzed by IB against the indicated antigens and by an RT-PCR reaction to monitor splicing of XBP1u mRNA (Calfon et al., 2002), respectively.